StandardEnvironment源码解析
write by donaldhan, 2018-01-10 14:32引言
应用事件多播器ApplicationEventMulticaster主要提供了应用事件监听器的管理操作(添加、移除),同时提供了发布应用事件到所管理的应用监听器的操作。应用事件多播器典型应用,为代理应用上下文,发布相关应用事件。BeanClassLoaderAware主要体用了设置bean类加载器的操作,主要用于框架实现类想用根据的name获取bean的应用类型的场景。
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster内部有一个存放监听器的集合 ListenerRetriever,事件监听器缓存retrieverCache(ConcurrentHashMap<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever>)用于存放应用事件与监听器映射关系,bean类加载器 ClassLoader,所属bean工厂BeanFactory 用于获取监听器bean name对应的监听器。所有的监听器注册操作实际由 ListenerRetriever 来完成,ListenerRetriever 使用LinkedHashSet来管理监听器。注意在每次添加和移除监听器之后,将会清除监听器缓存。抽象应用事件多播器除了管理监听器相关的实现此外,提供了获取注册到多播器监听器的方法,实际为ListenerRetriever整合 内部监听器集和监听器bean name对应的监听器;同时还有获取给定事件类型的对应的监听器,即关注给定事件类型的监听器,这过程首先从监听器缓存 中获取事件相关的监听器,如果存在,则从监听器检索器中检索出关闭事件的监听器,并封装在监听器检索器ListenerRetriever中,然后添加到监听器缓存中。 监听器缓存键ListenerCacheKey为事件类型与事件源的封装。
简单事件多播器,主要实现了多播器的多播事件操作,即将应用事件传递给相应的应用监听器,非关注 此事件的监听器,将会被忽略。默认情况下,简单事件多播器在当前线程下调用监听器的事件处理器操作,当然我们也可以设置多播器的任务执行器 Executor,委托任务执行器 调用监听器的事件处理器操作,同时我们也可以设置异常处理器 ErrorHandler 用于处理调用监听器过程中异常。
上一篇文章我们分析应用事件多播器的作用及默认实现SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,抽象应用上下文默认使用的多播器为SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster。 今天我们来看抽象应用上下为文的设计的另外一个模块的实现,及标准环境配置StandardEnvironment定义。
目录
StandardEnvironment定义
源码参见:StandardEnvironment
我们先来看标准环境的父类AbstractEnvironment:
AbstractEnvironment
源码参见:AbstractEnvironment
package org.springframework.core.env;
import java.security.AccessControlException;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.core.SpringProperties;
import org.springframework.core.convert.support.ConfigurableConversionService;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
*AbstractEnvironment为环境接口的抽象实现类。支持预留默认配置名,通过系统属性{@link #ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME} and
* {@link #DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME}开启指定的激活或默认配置。
* 具体子类主要的不同点在默认添加属性源这一点。抽象环境默认不添加。子类可以通过{@link #customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources)}
* hook,添加属性源,然而客户端应该使用 {@link ConfigurableEnvironment#getPropertySources()}定制,或依赖于{@link MutablePropertySources}
* 的API。
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment
* @see StandardEnvironment
*/
public abstract class AbstractEnvironment implements ConfigurableEnvironment {
/**
* 系统属性,用于通知spring忽略系统环境变量,比如坚决不会尝试使用{@link System#getenv()}
* 检索一个变量。
* 默认为false,如果spring的环境属性不能解决一个属性,将会降级到系统环境变量。如果你想
* 体验来之spring的{@code getenv} 的方法调用输出警告,可以考虑切换此标志为true。
* 比如在WebSphere的安全管理器设置和访问控制异常。
* @see #suppressGetenvAccess()
*/
public static final String IGNORE_GETENV_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.getenv.ignore";
/**
* 当前激活配置的属性的name。具体name可以逗号分开。
* 注意:确定的shell环境,比如bash是不允许在变量名中使用分割符的。假设使用的是spring的系统环境属性源
* {@link SystemEnvironmentPropertySource},此属性可以通过{@code SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE}来指定。
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles
*/
public static final String ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.profiles.active";
/**
* Spring环境配置,默认的激活配置名
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setDefaultProfiles
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.profiles.default";
/**
* 默认配置预留名的值。如果没有显示指定默认的配置名,或没有显示设置激活的配置名,默认的配置
* 将会被自动激活。
* @see #getReservedDefaultProfiles
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setDefaultProfiles
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles
* @see AbstractEnvironment#DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
* @see AbstractEnvironment#ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
*/
protected static final String RESERVED_DEFAULT_PROFILE_NAME = "default";
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
/**
* 激活配置解
*/
private final Set<String> activeProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
/**
* 默认的配置集
*/
private final Set<String> defaultProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<String>(getReservedDefaultProfiles());
/**
* 属性源管理器
*/
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources(this.logger);
/**
* 属性源解决器
*/
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver =
new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
/**
* Create a new {@code Environment} instance, calling back to
* {@link #customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources)} during construction to
* allow subclasses to contribute or manipulate {@link PropertySource} instances as
* appropriate.
* 创建一个新的环境实例,在构造期间,回调customizePropertySources方法,允许子类操作数据源实例。
* @see #customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources)
*/
public AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initialized " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " with PropertySources " + this.propertySources);
}
}
/**
*定制属性源对象集,以便在获取属性等相关方法时,通过环境来搜索。
* 子类重写此方法时,鼓励使用{@link MutablePropertySources#addLast(PropertySource)}方法
* 添加属性源,也可以调用父类的方法。
* <pre class="code">
* public class Level1Environment extends AbstractEnvironment {
* @Override
* protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
* super.customizePropertySources(propertySources); // no-op from base class
* propertySources.addLast(new PropertySourceA(...));
* propertySources.addLast(new PropertySourceB(...));
* }
* }
*
* public class Level2Environment extends Level1Environment {
* @Override
* protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
* super.customizePropertySources(propertySources); // add all from superclass
* propertySources.addLast(new PropertySourceC(...));
* propertySources.addLast(new PropertySourceD(...));
* }
* }
* </pre>
* 在上面的实现中,属性将会根据属性源的顺序A, B, C, D去解决。也就是说,属性源A优先于属性源D。如果Level2Environment
* 希望给定的属性源C、D先用A和B,可以调用在添加自己属性源的后面,调用{@code super.customizePropertySources}。
* <pre class="code">
* public class Level2Environment extends Level1Environment {
* @Override
* protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
* propertySources.addLast(new PropertySourceC(...));
* propertySources.addLast(new PropertySourceD(...));
* super.customizePropertySources(propertySources); // add all from superclass
* }
* }
* </pre>
*现在的搜索属性为C, D, A, B。
*除了这些建议之外,子类可以使用{@link MutablePropertySources}的任务添加,移除,替换定制自己需要的属性源的顺序。
* 基本的实现,没有属性注册。
* 注意:{@link ConfigurableEnvironment}的客户端,可以通过{@link #getPropertySources()}
* 方法进一步地定制属性源,典型的为在应用上下文初始化中ApplicationContextInitializer。比如:
* <pre class="code">
* ConfigurableEnvironment env = new StandardEnvironment();
* env.getPropertySources().addLast(new PropertySourceX(...));
* </pre>
* 实例变量访问警告
*在子类中声明的实例变量,拥有一个默认的初始化值,不应该通过此方法访问。由于java对象创建声明周期的限制,当通过
* {@link #AbstractEnvironment()}构造方法,回调自方法前,还没有初始化,可能导致一个空指针异常。如果需要
* 访问默认的初始化值,则直接在子类中执行属性源的初始化。注意:初始化实例的值时,不要出现任何问题,仅仅尝试访问默认值。
* @see MutablePropertySources
* @see PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer
*/
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
}
}
从上面可以看出,AbstractEnvironment主要的成员变量为激活配置集activeProfiles(LinkedHashSet
来看一下激活配置和默认配置的相关操作
/**
* 返回预留的默认配置名集。此处实现返回{@value #RESERVED_DEFAULT_PROFILE_NAME}。
* 子类为了定制预留的name,可以重写此方法。
* @see #RESERVED_DEFAULT_PROFILE_NAME
* @see #doGetDefaultProfiles()
*/
protected Set<String> getReservedDefaultProfiles() {
return Collections.singleton(RESERVED_DEFAULT_PROFILE_NAME);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of ConfigurableEnvironment interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* ConfigurableEnvironment接口的实现
*/
@Override
public String[] getActiveProfiles() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(doGetActiveProfiles());
}
/**
* 返回通过{@link #setActiveProfiles}方法,显示地设置激活配置集,如果当前激活配置集为空,则检查
* {@value #ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME}属性对应的激活配置。
* @see #getActiveProfiles()
* @see #ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
*/
protected Set<String> doGetActiveProfiles() {
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
/*
* 如果当前激活配置为空,则获取ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME的属性对应的配置,
* 并将属性值以逗号为分隔转换为激活配置。
*/
if (this.activeProfiles.isEmpty()) {
String profiles = getProperty(ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profiles)) {
setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(profiles)));
}
}
return this.activeProfiles;
}
}
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles(java.lang.String[])
*/
@Override
public void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notNull(profiles, "Profile array must not be null");
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
this.activeProfiles.clear();
for (String profile : profiles) {
validateProfile(profile);
this.activeProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment#addActiveProfile(java.lang.String)
*/
@Override
public void addActiveProfile(String profile) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Activating profile '" + profile + "'");
}
validateProfile(profile);
doGetActiveProfiles();
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
this.activeProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see org.springframework.core.env.Environment#getDefaultProfiles()
*/
@Override
public String[] getDefaultProfiles() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(doGetDefaultProfiles());
}
/**
* 返回通过{@link #setDefaultProfiles(String...)}显示设置的默认配置,如果当前默认配置集,仅包含
* 预留配置,则进一步检查DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME属性对应的配置
* @see #AbstractEnvironment()
* @see #getDefaultProfiles()
* @see #DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
* @see #getReservedDefaultProfiles()
*/
protected Set<String> doGetDefaultProfiles() {
synchronized (this.defaultProfiles) {
if (this.defaultProfiles.equals(getReservedDefaultProfiles())) {
String profiles = getProperty(DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profiles)) {
setDefaultProfiles(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(profiles)));
}
}
return this.defaultProfiles;
}
}
/**
* 如果没有其他的配置显示地设置,则设置默认的配置。
* 调用此方法,将会移除在环境构造的过程中已经添加的默认配置。
* @see #AbstractEnvironment()
* @see #getReservedDefaultProfiles()
*/
@Override
public void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notNull(profiles, "Profile array must not be null");
synchronized (this.defaultProfiles) {
this.defaultProfiles.clear();
for (String profile : profiles) {
validateProfile(profile);
this.defaultProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see org.springframework.core.env.Environment#acceptsProfiles(java.lang.String[])
*/
@Override
public boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notEmpty(profiles, "Must specify at least one profile");
for (String profile : profiles) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(profile) && profile.charAt(0) == '!') {
if (!isProfileActive(profile.substring(1))) {
return true;
}
}
else if (isProfileActive(profile)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断给定配置是否激活,如果激活配置为空,则使用默认的配置进行判断
* @throws IllegalArgumentException per {@link #validateProfile(String)}
*/
protected boolean isProfileActive(String profile) {
validateProfile(profile);
Set<String> currentActiveProfiles = doGetActiveProfiles();
return (currentActiveProfiles.contains(profile) ||
(currentActiveProfiles.isEmpty() && doGetDefaultProfiles().contains(profile)));
}
/**
* 校验给定的环境配置,内部使用,在添加激活和默认配置前调用。
* 子类可以重此方法,以便进一步的限制配置语义。如果配置为null, empty, whitespace-only或以非操作符开头,
* 则抛出非法参数异常。
* @see #acceptsProfiles
* @see #addActiveProfile
* @see #setDefaultProfiles
*/
protected void validateProfile(String profile) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(profile)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid profile [" + profile + "]: must contain text");
}
if (profile.charAt(0) == '!') {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid profile [" + profile + "]: must not begin with ! operator");
}
}
从上来看,激活配置与默认配置的相关操作实际为相关配置集集合操作。
再来看整合属性源操作及其他操作。
@Override
public void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent) {
//添加父环境配置中的属性源,到本环境配置属性源集的链尾
for (PropertySource<?> ps : parent.getPropertySources()) {
if (!this.propertySources.contains(ps.getName())) {
this.propertySources.addLast(ps);
}
}
//添加父环境的激活配置到当前激活配置集
String[] parentActiveProfiles = parent.getActiveProfiles();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parentActiveProfiles)) {
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
for (String profile : parentActiveProfiles) {
this.activeProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
//添加父环境的默认配置到当前默认配置集
String[] parentDefaultProfiles = parent.getDefaultProfiles();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parentDefaultProfiles)) {
synchronized (this.defaultProfiles) {
this.defaultProfiles.remove(RESERVED_DEFAULT_PROFILE_NAME);
for (String profile : parentDefaultProfiles) {
this.defaultProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 属性源集
*/
@Override
public MutablePropertySources getPropertySources() {
return this.propertySources;
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment() {
if (suppressGetenvAccess()) {//如果不可以访问系统属性,则返回空Map
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
try {
//否则获取系统属性
return (Map) System.getenv();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return (Map) new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Override
protected String getSystemAttribute(String attributeName) {
try {
return System.getenv(attributeName);
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Caught AccessControlException when accessing system environment variable '" +
attributeName + "'; its value will be returned [null]. Reason: " + ex.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
}
};
}
}
/**
* Determine whether to suppress {@link System#getenv()}/{@link System#getenv(String)}
* access for the purposes of {@link #getSystemEnvironment()}.
* 判断是否可以通过{@link System#getenv()}/{@link System#getenv(String)}方法,访问系统属性。
* <p>If this method returns {@code true}, an empty dummy Map will be used instead
* of the regular system environment Map, never even trying to call {@code getenv}
* and therefore avoiding security manager warnings (if any).
* 如果返回true,则一个空的伪Map集将作为系统环境Map,设置不能调用{@code getenv}方法,进一步避免安全管理器警告。
* <p>The default implementation checks for the "spring.getenv.ignore" system property,
* returning {@code true} if its value equals "true" in any case.
* 默认实现检查系统属性spring.getenv.ignore,如果属性值为true,则返回true。
* @see #IGNORE_GETENV_PROPERTY_NAME
* @see SpringProperties#getFlag
*/
protected boolean suppressGetenvAccess() {
return SpringProperties.getFlag(IGNORE_GETENV_PROPERTY_NAME);
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
public Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties() {
try {
return (Map) System.getProperties();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return (Map) new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Override
protected String getSystemAttribute(String attributeName) {
try {
return System.getProperty(attributeName);
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Caught AccessControlException when accessing system property '" +
attributeName + "'; its value will be returned [null]. Reason: " + ex.getMessage());
}
return null;
}
}
};
}
}
从上面来看,整合环境操作,主要是整合属性源,激活配置与默认配置。
再来看ConfigurablePropertyResolver和PropertyResolver接口的实现
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of ConfigurablePropertyResolver interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 可配置属性配置接口ConfigurablePropertyResolver的实现
*/
@Override
public ConfigurableConversionService getConversionService() {
return this.propertyResolver.getConversionService();
}
@Override
public void setConversionService(ConfigurableConversionService conversionService) {
this.propertyResolver.setConversionService(conversionService);
}
@Override
public void setPlaceholderPrefix(String placeholderPrefix) {
this.propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(placeholderPrefix);
}
@Override
public void setPlaceholderSuffix(String placeholderSuffix) {
this.propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(placeholderSuffix);
}
@Override
public void setValueSeparator(String valueSeparator) {
this.propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(valueSeparator);
}
@Override
public void setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(boolean ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders) {
this.propertyResolver.setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders);
}
@Override
public void setRequiredProperties(String... requiredProperties) {
this.propertyResolver.setRequiredProperties(requiredProperties);
}
@Override
public void validateRequiredProperties() throws MissingRequiredPropertiesException {
this.propertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of PropertyResolver interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 属性解决器接口PropertyResolver的实现
*/
@Override
public boolean containsProperty(String key) {
return this.propertyResolver.containsProperty(key);
}
@Override
public String getProperty(String key) {
return this.propertyResolver.getProperty(key);
}
@Override
public String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue) {
return this.propertyResolver.getProperty(key, defaultValue);
}
@Override
public <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) {
return this.propertyResolver.getProperty(key, targetType);
}
@Override
public <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue) {
return this.propertyResolver.getProperty(key, targetType, defaultValue);
}
@Override
@Deprecated
public <T> Class<T> getPropertyAsClass(String key, Class<T> targetType) {
return this.propertyResolver.getPropertyAsClass(key, targetType);
}
@Override
public String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException {
return this.propertyResolver.getRequiredProperty(key);
}
@Override
public <T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException {
return this.propertyResolver.getRequiredProperty(key, targetType);
}
@Override
public String resolvePlaceholders(String text) {
return this.propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(text);
}
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}
从上面可以看出,ConfigurablePropertyResolver和PropertyResolver接口的实现实际委托个内部的属性源解决器propertyResolver。
来小节一下:
AbstractEnvironment主要的成员变量为激活配置集activeProfiles(LinkedHashSet
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver我们方法后面再简单讲一下,我们把标注环境先讲完
package org.springframework.core.env;
/**
* 非web应用的环境变量标准实现。
* 另外添加了可配置环境的一般功能,比如属性解决,配置相关操作,此实现提供了两个默认的属性源,搜索顺序如下:
* <ul>
* <li>{@linkplain AbstractEnvironment#getSystemProperties() system properties}
* <li>{@linkplain AbstractEnvironment#getSystemEnvironment() system environment variables}
* </ul>
*
*也就是说,如果一个属性"xyz"在当前继承中的虚拟机系统属性源和环境变量属性源中都存在,则系统属性源中的属性将会被返回。
*
*默认的属性源可以被移除,重排序,替代,同时可以使用{@link #getPropertySources()}方法,返回的
*SystemEnvironmentPropertySource用于处理Shell环境变量属性name,比如Bash。
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.1
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment
* @see SystemEnvironmentPropertySource
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.StandardServletEnvironment
*/
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {
/** System environment property source name: {@value} 系统环境变量属性源name*/
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
/** JVM system properties property source name: {@value} java虚拟机系统属性源name*/
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
/**
* 定制属性源集:
* <ul>
* <li>{@value #SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME}
* <li>{@value #SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME}
* </ul>
* 虚拟机系统属性源优于系统环境变量属性源。
* @see AbstractEnvironment#customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources)
* @see #getSystemProperties()
* @see #getSystemEnvironment()
*/
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
}
从上面可以看出,StandardEnvironment的默认属性源集有系统属性源和环境变量属性源。 关于Map属性源[MapPropertySource][]和系统环境变量属性源[SystemEnvironmentPropertySource][],我们这里就不说,点击,可以查看相关源码。
抽象环境声明中有一个性源解决器属性
/**
* 属性源解决器
*/
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver =
new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
我们再来简单看一下PropertySourcesPropertyResolver:先来看起父类抽象属性解决器
AbstractPropertyResolver
package org.springframework.core.env;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService;
import org.springframework.core.convert.support.ConfigurableConversionService;
import org.springframework.core.convert.support.DefaultConversionService;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.PropertyPlaceholderHelper;
import org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils;
/**
* Abstract base class for resolving properties against any underlying source.
* 依据任何底层属性源解属性值的抽象属性解决器AbstractPropertyResolver。
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
*/
public abstract class AbstractPropertyResolver implements ConfigurablePropertyResolver {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private volatile ConfigurableConversionService conversionService;//可配转换服务
private PropertyPlaceholderHelper nonStrictHelper;//非严格属性占位符工具,遇到不可解决的占位符,跳过
private PropertyPlaceholderHelper strictHelper;//严格属性占位符工具,遇到不可解决的占位符,抛出异常
private boolean ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders = false;//是否忽略不可解决的占位符
private String placeholderPrefix = SystemPropertyUtils.PLACEHOLDER_PREFIX;//占位符前缀
private String placeholderSuffix = SystemPropertyUtils.PLACEHOLDER_SUFFIX;//占位符后缀
private String valueSeparator = SystemPropertyUtils.VALUE_SEPARATOR;//占位符key与默认值之间的分隔符
/**
* 必须的属性集
*/
private final Set<String> requiredProperties = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
@Override
public ConfigurableConversionService getConversionService() {
// Need to provide an independent DefaultConversionService, not the
// shared DefaultConversionService used by PropertySourcesPropertyResolver.
if (this.conversionService == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (this.conversionService == null) {
this.conversionService = new DefaultConversionService();
}
}
}
return conversionService;
}
@Override
public void setConversionService(ConfigurableConversionService conversionService) {
Assert.notNull(conversionService, "ConversionService must not be null");
this.conversionService = conversionService;
}
...
@Override
public boolean containsProperty(String key) {
return (getProperty(key) != null);
}
@Override
public String getProperty(String key) {
return getProperty(key, String.class);
}
@Override
public String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue) {
String value = getProperty(key);
return (value != null ? value : defaultValue);
}
...
/**
* Convert the given value to the specified target type, if necessary.
* 如果需要,转换给定值为目标类型
* @param value the original property value
* @param targetType the specified target type for property retrieval
* @return the converted value, or the original value if no conversion
* is necessary
* @since 4.3.5
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T convertValueIfNecessary(Object value, Class<T> targetType) {
if (targetType == null) {
return (T) value;
}
ConversionService conversionServiceToUse = this.conversionService;
if (conversionServiceToUse == null) {
// Avoid initialization of shared DefaultConversionService if
// no standard type conversion is needed in the first place...
/*
* 如果不需要标准的类型转换,则避免初始化共享默认转换服务
*/
if (ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(targetType, value)) {
return (T) value;
}
//获取默认的共享转换服务实例
conversionServiceToUse = DefaultConversionService.getSharedInstance();
}
return conversionServiceToUse.convert(value, targetType);
}
/**
* Retrieve the specified property as a raw String,
* i.e. without resolution of nested placeholders.
* 获取属性key对应的原始String类型的值
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @return the property value or {@code null} if none found
*/
protected abstract String getPropertyAsRawString(String key);
}
从上面可以看出,抽象属性解决器成员为转换器服务conversionService(ConfigurableConversionService),默认为DefaultConversionService。 抽象属性解决器主要所做的工作为从属性源中加载相关的属性,替代给定文中的占位符。
关于类型转换器
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
源码参见:PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
package org.springframework.core.env;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionException;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
/**
* {@link PropertyResolver} implementation that resolves property values against
* an underlying set of {@link PropertySources}.
* 依赖于底层的属性源集,解决属性值。
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
* @see PropertySource
* @see PropertySources
* @see AbstractEnvironment
*/
public class PropertySourcesPropertyResolver extends AbstractPropertyResolver {
private final PropertySources propertySources;//属性源集
/**
* Create a new resolver against the given property sources.
* @param propertySources the set of {@link PropertySource} objects to use
*/
public PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(PropertySources propertySources) {
this.propertySources = propertySources;
}
@Override
public boolean containsProperty(String key) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) {
if (propertySource.containsProperty(key)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String getProperty(String key) {
return getProperty(key, String.class, true);
}
@Override
public <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType) {
return getProperty(key, targetValueType, true);
}
@Override
protected String getPropertyAsRawString(String key) {
return getProperty(key, String.class, false);
}
/**
* @param key
* @param targetValueType
* @param resolveNestedPlaceholders 是否解决嵌入式的值
* @return
*/
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
for (PropertySource<?> propertySource : this.propertySources) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Searching for key '" + key + "' in PropertySource '" +
propertySource.getName() + "'");
}
//获取属性值
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) {
//解决值的的占位符
value = resolveNestedPlaceholders((String) value);
}
//输出key发现日志
logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value);
//转换给定的值,为目标类型值
return convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType);
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source");
}
return null;
}
}
从上面可以看出,PropertySourcesPropertyResolver内部有一个属性源集propertySources(PropertySources),这个就是在AbstractEnvironment的 变量属性源解决器propertyResolver(PropertySourcesPropertyResolver)声明中,定义的实际为MutablePropertySources,即环境的属性源。 在获取属性的过程中,如果需要类型转换,则委托给内部转换器服务,默认为DefaultConversionService。
我们再来简单看一下DefaultConversionService,在讲之前先来看,其父类GenericConversionService。
GenericConversionService
package org.springframework.core.convert.support;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.core.DecoratingProxy;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionException;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionFailedException;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConverterNotFoundException;
import org.springframework.core.convert.TypeDescriptor;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.ConditionalConverter;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.ConditionalGenericConverter;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.ConverterFactory;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.ConverterRegistry;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.GenericConverter;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.GenericConverter.ConvertiblePair;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ConcurrentReferenceHashMap;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* Base {@link ConversionService} implementation suitable for use in most environments.
* Indirectly implements {@link ConverterRegistry} as registration API through the
* {@link ConfigurableConversionService} interface.
* GenericConversionService用于大多数环境中的类型转换服务基础实现类。
* 通过ConfigurableConversionService直接实现了转换器注册接口
* @author Keith Donald
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author David Haraburda
* @since 3.0
*/
public class GenericConversionService implements ConfigurableConversionService {
/**
* General NO-OP converter used when conversion is not required.
* 当不需要转换时,使用NO-OP转换器
*/
private static final GenericConverter NO_OP_CONVERTER = new NoOpConverter("NO_OP");
/**
* Used as a cache entry when no converter is available.
* This converter is never returned.
* 当没有转换器可以用,使用NoOpConverter作为一个缓存Entry
*/
private static final GenericConverter NO_MATCH = new NoOpConverter("NO_MATCH");
/** Java 8's java.util.Optional.empty() */
private static Object javaUtilOptionalEmpty = null;
static {
try {
//加载Optional,获取空对象
Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName("java.util.Optional", GenericConversionService.class.getClassLoader());
javaUtilOptionalEmpty = ClassUtils.getMethod(clazz, "empty").invoke(null);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Java 8 not available - conversion to Optional not supported then.
}
}
//转化器
private final Converters converters = new Converters();
//转换器缓存
private final Map<ConverterCacheKey, GenericConverter> converterCache =
new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<ConverterCacheKey, GenericConverter>(64);
...
/**
* Manages all converters registered with the service.
* 管理当前注册到服务的所有转换器
*/
private static class Converters {
/**
* 全局转换器,存放没有转换pair的转换器,即条件转换器
*/
private final Set<GenericConverter> globalConverters = new LinkedHashSet<GenericConverter>();
/**
* 源类型与目标类型对ConvertiblePair的转换器ConvertersForPair映射
*/
private final Map<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair> converters =
new LinkedHashMap<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair>(36);
...
}
}
我们只看GenericConversionService的内部变量,如果看相关的转换器注册和类型转换操作,参见源码。
从上面可以看出,GenericConversionService主要使用Converters来管理类型转换器,Converters的内部主要有两个集合来存放转换器,
一个是条件转换器集globalConverters( LinkedHashSet
再来看DefaultConversionService
DefaultConversionService
package org.springframework.core.convert.support;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Currency;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.UUID;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.ConverterRegistry;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
/**
* A specialization of {@link GenericConversionService} configured by default
* with converters appropriate for most environments.
*DefaultConversionService为转换器的默认是实现,提供了大多数环境使用的转换器。
* <p>Designed for direct instantiation but also exposes the static
* {@link #addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry)} utility method for ad-hoc
* use against any {@code ConverterRegistry} instance.
*直接实例化设置模式,但是提供了添加默认转换器的静态便利方法。
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 3.1
*/
public class DefaultConversionService extends GenericConversionService {
/** Java 8's java.util.Optional class available? Optional是否可使用*/
private static final boolean javaUtilOptionalClassAvailable =
ClassUtils.isPresent("java.util.Optional", DefaultConversionService.class.getClassLoader());
/** Java 8's java.time package available? 事件包是否可利用*/
private static final boolean jsr310Available =
ClassUtils.isPresent("java.time.ZoneId", DefaultConversionService.class.getClassLoader());
/** Java 8's java.util.stream.Stream class available? Stream是否可用 */
private static final boolean streamAvailable = ClassUtils.isPresent(
"java.util.stream.Stream", DefaultConversionService.class.getClassLoader());
private static volatile DefaultConversionService sharedInstance;//共享转换器实例
/**
* Create a new {@code DefaultConversionService} with the set of
* {@linkplain DefaultConversionService#addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry) default converters}.
* 根据默认的转换器集,创建一个默认转换器实例
*/
public DefaultConversionService() {
addDefaultConverters(this);
}
/**
* Return a shared default {@code ConversionService} instance,
* lazily building it once needed.
* 返回默认转换器服务的默认实例,懒加载方法创建实例。
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> We highly recommend constructing individual
* {@code ConversionService} instances for customization purposes.
* 注意:我们将强烈建议为特殊的用途构造单独的转化器服务
* This accessor is only meant as a fallback for code paths which
* need simple type coercion but cannot access a longer-lived
* {@code ConversionService} instance any other way.
*
* @return the shared {@code ConversionService} instance (never {@code null})
* @since 4.3.5
*/
public static ConversionService getSharedInstance() {
if (sharedInstance == null) {
synchronized (DefaultConversionService.class) {
if (sharedInstance == null) {
sharedInstance = new DefaultConversionService();
}
}
}
return sharedInstance;
}
/**
* Add converters appropriate for most environments.
* 添加大多数环境使用的转化器
* @param converterRegistry the registry of converters to add to
* (must also be castable to ConversionService, e.g. being a {@link ConfigurableConversionService})
* @throws ClassCastException if the given ConverterRegistry could not be cast to a ConversionService
*/
public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
addScalarConverters(converterRegistry);
addCollectionConverters(converterRegistry);
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ByteBufferConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
if (jsr310Available) {
Jsr310ConverterRegistrar.registerJsr310Converters(converterRegistry);
}
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToObjectConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new IdToEntityConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new FallbackObjectToStringConverter());
if (javaUtilOptionalClassAvailable) {
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToOptionalConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
}
}
/**
* Add common collection converters.
* 添加一般的集合转换器
* @param converterRegistry the registry of converters to add to
* (must also be castable to ConversionService, e.g. being a {@link ConfigurableConversionService})
* @throws ClassCastException if the given ConverterRegistry could not be cast to a ConversionService
* @since 4.2.3
*/
public static void addCollectionConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
ConversionService conversionService = (ConversionService) converterRegistry;
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToArrayConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToArrayConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new MapToMapConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToStringConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToArrayConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ArrayToObjectConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToArrayConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToStringConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new CollectionToObjectConverter(conversionService));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToCollectionConverter(conversionService));
if (streamAvailable) {
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StreamConverter(conversionService));
}
}
/**
* 添加平级转换器
* @param converterRegistry
*/
private static void addScalarConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new NumberToNumberConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new StringToNumberConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Number.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCharacterConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Character.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new NumberToCharacterConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new CharacterToNumberFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToBooleanConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Boolean.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new StringToEnumConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new EnumToStringConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverterFactory(new IntegerToEnumConverterFactory());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new EnumToIntegerConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToLocaleConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Locale.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCharsetConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Charset.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToCurrencyConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(Currency.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToPropertiesConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new PropertiesToStringConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToUUIDConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(UUID.class, String.class, new ObjectToStringConverter());
}
/**
* Inner class to avoid a hard-coded dependency on Java 8's {@code java.time} package.
* 时间转换器
*/
private static final class Jsr310ConverterRegistrar {
public static void registerJsr310Converters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
converterRegistry.addConverter(new StringToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZoneIdToTimeZoneConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ZonedDateTimeToCalendarConverter());
}
}
}
从上面来看,DefaultConversionService内部有一个懒加载的共享实例,DefaultConversionService内部添加大多数环境需要使用的 转化器,如原始类型,及集合类转换器。
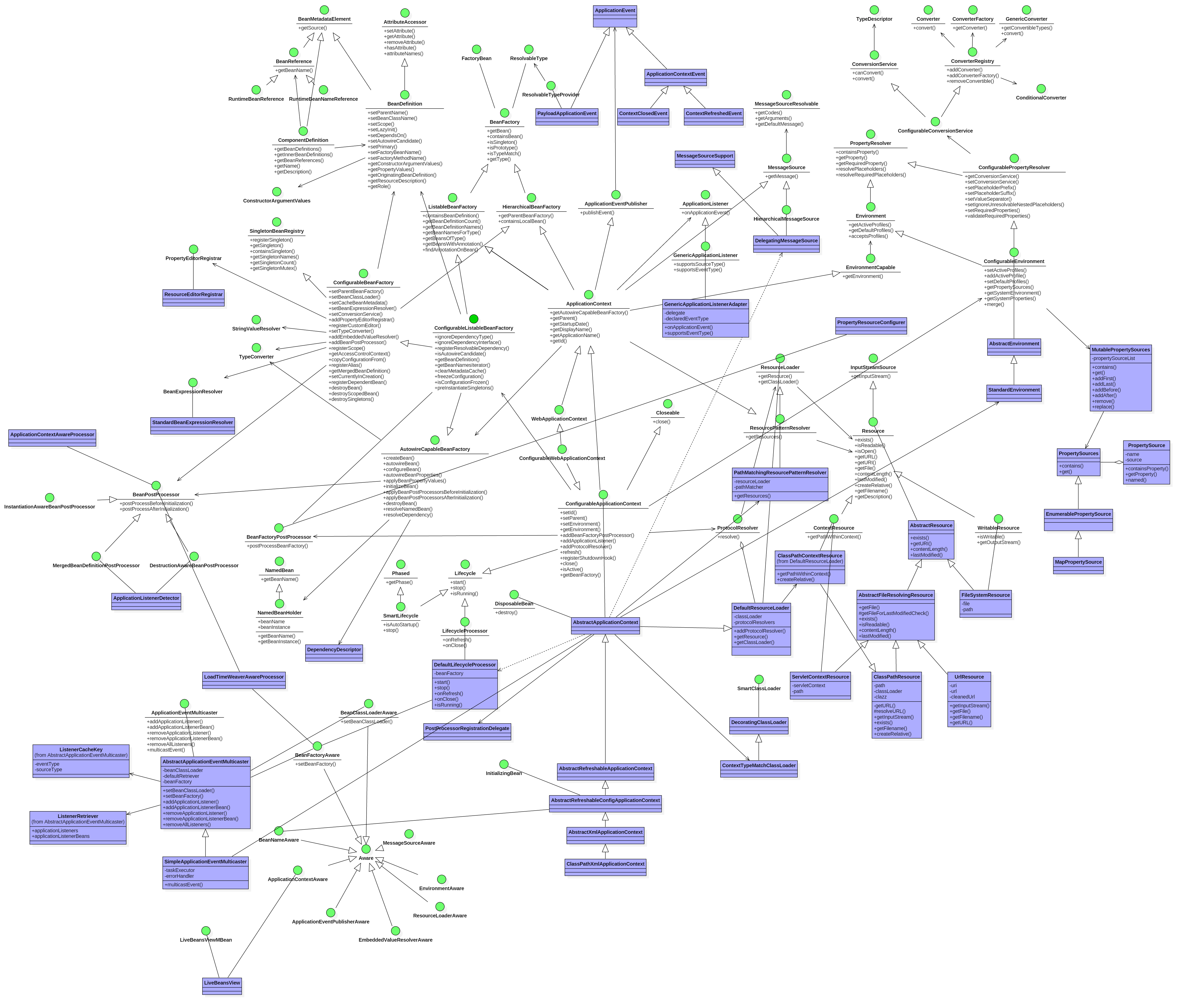
最后我们以StandardEnvironment的类图结束这篇文章。

总结
AbstractEnvironment主要的成员变量为激活配置集activeProfiles(LinkedHashSet
AbstractPropertyResolver抽象属性解决器主要,主要是从属性源中加载相关的属性,替代给定文中的占位符。
抽象属性解决器成员为转换器服务conversionService(ConfigurableConversionService),默认为DefaultConversionService。 抽象属性解决器主要所做的工作为从属性源中加载相关的属性,替代给定文中的占位符。
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver内部有一个属性源集propertySources(PropertySources),为在AbstractEnvironment的 变量属性源解决器propertyResolver(PropertySourcesPropertyResolver)声明中,定义的实际为MutablePropertySources,即环境的属性源。 在获取属性的过程中,如果需要类型转换,则委托给内部转换器服务,默认为DefaultConversionService。
GenericConversionService主要使用Converters来管理类型转换器,Converters的内部主要有两个集合来存放转换器,
一个是条件转换器集globalConverters( LinkedHashSet
DefaultConversionService内部有一个懒加载的共享实例,DefaultConversionService内部添加大多数环境需要使用的 转化器,如原始类型,及集合类转换器。