SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster解析
write by donaldhan, 2018-01-06 15:17引言
抽象应用上下文 AbstractApplicationContext 实际为一个可配置上下文 ConfigurableApplicationContext 和可销毁的bean(DisposableBean),同时拥有了资源加载功能(DefaultResourceLoader)。我们通过一个唯一的id标注抽象上下文,同时抽象上下文拥有一个展示名。除此身份识别属性之前,抽象应用上下文,有一个父上下文 ApplicationContext ,可配的环境配置 ConfigurableEnvironment ,bean工厂后处理器集(List
路径匹配资源模式解决器PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver内部有一个Ant路径匹配器 AntPathMatcher,和一个资源类加载器,资源加载器可以 使用所属上下文中的资源加载器,也可以为给定类加载器的DefaultResourceLoader。路径匹配资源模式解决器主要提供了加载给定路径位置的资源方法,此方法可以解决无通配符的路径位置模式({@code file:C:/context.xml},{@code classpath:/context.xml},{@code /WEB-INF/context.xml}”),也可以解决包含Ant风格的通配符路径位置模式资源({@code classpath:META-INF/beans.xml}),主要以classpath为前缀的路径位置模式,资源加载器将会查找类路径下所有相同name对应的资源文件,包括子目录和jar包。如果明确的加载资源,可以使用{@code classpath:/context.xml}形式路径模式,如果想要探测类路径下的所有name对应的资源文件,可以使用形式路径模式。
BeanFactoryAware接口主要提供设置bean工厂操作。LifecycleProcessor接口主要提供了通知上下文刷新和关闭的操作。Phased主要提供了获取组件阶段值操作。 SmartLifecycle接口主要提供关闭回调操作,在组件停止后,调用回调接口。并提供了判断组件在容器上下文刷新时,组件是否自动刷新的操作。
默认生命周期处理器DefaultLifecycleProcessor,内部主要有3个成员变量,一个是运行状态标识,一个是生命周期bean关闭超时时间,还有一个是所属的bean工厂。默认生命周期处理器,启动生命周期bean的过程为,将生命周期bean,按阶段值分组,并从阶段值从小到大,启动生命周期bean分组中bean。默认生命周期处理器,关闭生命周期bean的过程为,将生命周期bean,按阶段值分组,并从阶段值从大到小,关闭生命周期bean分组中bean。关闭生命周期bean的顺序与启动顺序正好相反。需要注意的是无论是启动还是关闭,生命周期bean所依赖的bean都是在其之前启动或关闭,忽略掉被依赖bean的Phase阶段值。对于非生命周期bean,其阶段值默认为0。

上一篇文章我们看了抽象应用上下文的内部变量声明与构造函数,同时看了一下默认的路径匹配资源模式解决器PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver和生命周期处理器DefaultLifecycleProcessor。 由于抽象应用上下文所设计的模块较多,我们不得不分模块来分析,今天我们来看另一个模块应用事件多播器。
目录
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster定义
源码参见:SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
在看SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster定义之前,我们来看一下其父接口定义
ApplicationEventMulticaster
源码参见:ApplicationEventMulticaster
package org.springframework.context.event;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
/**
*应用事件多播器ApplicationEventMulticaster的实现可以管理多个应用监听器对象,
*并发布事件到相关监听器。
*应用事件多播器的使用典型场景,应用上下文可以使用应用事件多播器代理事件的发布事件操作。
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Stephane Nicoll
*/
public interface ApplicationEventMulticaster {
/**
* 添加监听器
* @param listener the listener to add
*/
void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
/**
* 添加监听器bean
* @param listenerBeanName the name of the listener bean to add
*/
void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName);
/**
* 移除监听器
* @param listener the listener to remove
*/
void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener);
/**
* 移除监听器bean
* @param listenerBeanName the name of the listener bean to add
*/
void removeApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName);
/**
* 移除所有注册到多播器的监听器。
* 在移除所有监听器操作调用后,多播器对于发生的事件不做任何处理,直到有新的监听器注册
*/
void removeAllListeners();
/**
* 多播给定的应用事件到相关监听器
* 如果想要尽可能中的支持一般的事件,可以考虑使用{@link #multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent, ResolvableType)}
* 方法。
* @param event the event to multicast
*/
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event);
/**
* Multicast the given application event to appropriate listeners.
* 多播给定的事件到关联监听器。
* 如果eventType类型为空,则将基于event实例 构建一个默认的类型
* @param event the event to multicast
* @param eventType the type of event (can be null)
* @since 4.2
*/
void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType);
}
从上面可以看出,应用事件多播器ApplicationEventMulticaster主要提供了应用事件监听器的管理操作(添加、移除),同时提供了发布应用事件到所管理的应用监听器的操作。 应用事件多播器典型应用,为代理应用上下文,发布相关应用事件。
BeanClassLoaderAware
源码参见:BeanClassLoaderAware
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
/**
* BeanClassLoaderAware接口回调,允许bean访问其的类加载器;也就是说当前bean工厂加载
* bean 类的类加载器。
* 主要用于框架实现类想要根据bean的name获取bean的应用类型,尽管框架实现类可能被共享类加载器加载。
* <p>For a list of all bean lifecycle methods, see the
* {@link BeanFactory BeanFactory javadocs}.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 2.0
* @see BeanNameAware
* @see BeanFactoryAware
* @see InitializingBean
*/
public interface BeanClassLoaderAware extends Aware {
/**
* 提供bean实例的类加载器回调。
* method or a custom init-method.
* 在正常的bean属性初始化之后,在是在
* {@link InitializingBean InitializingBean's}
* {@link InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}和一般初始化方法调用之前。
*
* @param classLoader the owning class loader; may be {@code null} in
* which case a default {@code ClassLoader} must be used, for example
* the {@code ClassLoader} obtained via
* {@link org.springframework.util.ClassUtils#getDefaultClassLoader()}
*/
void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader);
}
从上面可以看出,BeanClassLoaderAware主要体用了设置bean类加载器的操作,主要用于框架实现类想用根据的name获取bean的应用类型的场景。
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster
源码参见:AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster
package org.springframework.context.event;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.AopProxyUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
/**
*AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster为应用事件多播器的抽象实现接口,为基本的
*监听器注册提供了便利。
*默认情况下,因为多播器保存监听器在链表Set中,不允许相同监听器的多实例存在。如果需要,可以重写
*此管理监听器的功能。
*应用事件多播器的多播事件方法留给子类实现。SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster仅仅多播所有事件到
*所有监听器。其他的实现可以相对复杂。
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 1.2.3
* @see #getApplicationListeners(ApplicationEvent, ResolvableType)
* @see SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
*/
public abstract class AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster
implements ApplicationEventMulticaster, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware {
private final ListenerRetriever defaultRetriever = new ListenerRetriever(false);
final Map<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever> retrieverCache =
new ConcurrentHashMap<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever>(64);//监听器
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader; //bean类加载器
private BeanFactory beanFactory;//所属bean工厂
private Object retrievalMutex = this.defaultRetriever;//检索互斥对象
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = classLoader;
}
/**
* 设置多播器所属的bean工厂,如果bean工厂为ConfigurableBeanFactory,
* 且bean类加载为null,则使用工厂的bean类加载器;同时使用工厂的单例互斥对象。
*/
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
if (beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
ConfigurableBeanFactory cbf = (ConfigurableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
if (this.beanClassLoader == null) {
this.beanClassLoader = cbf.getBeanClassLoader();
}
this.retrievalMutex = cbf.getSingletonMutex();
}
}
private BeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
if (this.beanFactory == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ApplicationEventMulticaster cannot retrieve listener beans " +
"because it is not associated with a BeanFactory");
}
return this.beanFactory;
}
@Override
public void addApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
// Explicitly remove target for a proxy, if registered already,
// in order to avoid double invocations of the same listener.
//如果代理的目标监听器也已经注册到多播器,为了避免调用相同的监听器两次,
//显示地从多播器移除对应的目标监听器。
//获取代理监听器的目标对象实例
Object singletonTarget = AopProxyUtils.getSingletonTarget(listener);
if (singletonTarget instanceof ApplicationListener) {
//如果目标监听器为应用监听器,则从多播器中移除
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.remove(singletonTarget);
}
//添加监听器到多播器
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear();//清空多播器应用事件监听器缓存
}
}
@Override
public void addApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
//添加监听器bean name到多播器
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
this.retrieverCache.clear();//清空多播器应用事件监听器缓存
}
}
@Override
public void removeApplicationListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
//从多播器移除监听器
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.remove(listener);
this.retrieverCache.clear();//清空多播器应用事件监听器缓存
}
}
@Override
public void removeApplicationListenerBean(String listenerBeanName) {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
//从多播器移除监听器listenerBeanName
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.remove(listenerBeanName);
this.retrieverCache.clear();//清空多播器应用事件监听器缓存
}
}
@Override
public void removeAllListeners() {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
//清空多播器的应用监听器集和监听器bean name集
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners.clear();
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans.clear();
this.retrieverCache.clear();//清空多播器应用事件监听器缓存
}
}
...
/**
* Cache key for ListenerRetrievers, based on event type and source type.
* 基于事件类型和事件源类型的ListenerRetrievers缓存key。
*/
private static final class ListenerCacheKey implements Comparable<ListenerCacheKey> {
private final ResolvableType eventType;//事件类型
private final Class<?> sourceType;//事件源
public ListenerCacheKey(ResolvableType eventType, Class<?> sourceType) {
this.eventType = eventType;
this.sourceType = sourceType;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
ListenerCacheKey otherKey = (ListenerCacheKey) other;
return (ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.eventType, otherKey.eventType) &&
ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.sourceType, otherKey.sourceType));
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.eventType) * 29 + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.sourceType));
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ListenerCacheKey [eventType = " + this.eventType + ", sourceType = " + this.sourceType.getName() + "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(ListenerCacheKey other) {
int result = 0;
if (this.eventType != null) {
result = this.eventType.toString().compareTo(other.eventType.toString());
}
if (result == 0 && this.sourceType != null) {
result = this.sourceType.getName().compareTo(other.sourceType.getName());
}
return result;
}
}
/**
* Helper class that encapsulates a specific set of target listeners,
* allowing for efficient retrieval of pre-filtered listeners.
* 监听器集封装辅助类,考虑到预过滤监听的有效检索。
* <p>An instance of this helper gets cached per event type and source type.
* 辅助类可以缓存事件类型和事件源类型
*/
private class ListenerRetriever {
public final Set<ApplicationListener<?>> applicationListeners;//监听器集
public final Set<String> applicationListenerBeans;//监听器bean name集
private final boolean preFiltered; //是否预先过滤
public ListenerRetriever(boolean preFiltered) {
this.applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationListener<?>>();
this.applicationListenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
this.preFiltered = preFiltered;
}
/**
* 合并监听器name集对应的监听器和监听器集
* @return
*/
public Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners() {
LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>>();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.applicationListeners) {
allListeners.add(listener);
}
//遍历监听器name集,获取相应的监听器,如果需要添加到监听器集
if (!this.applicationListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : this.applicationListenerBeans) {
try {
//获取name对应的监听器
ApplicationListener<?> listener = beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
if (this.preFiltered || !allListeners.contains(listener)) {
//如果需要预过滤或者监听器集不包括对应的监听器,则添加监听器到监听器集
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Singleton listener instance (without backing bean definition) disappeared -
// probably in the middle of the destruction phase
}
}
}
//根据监听器注解Order的值进行排序,没有则为null
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
return allListeners;
}
}
}
从上面可以看出,AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster内部有一个存放监听器的集合 ListenerRetriever,事件监听器缓存retrieverCache(ConcurrentHashMap<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever>)用于存放应用事件与监听器映射关系,bean类加载器 ClassLoader,所属bean工厂BeanFactory 用于获取监听器bean name对应的监听器。所有的监听器注册操作实际由 ListenerRetriever 来完成,ListenerRetriever 使用LinkedHashSet来管理监听器。 注意在每次添加和移除监听器之后,将会清除监听器缓存。
再来看一下其他方法
/**
* Return a Collection containing all ApplicationListeners.
* 获取注册到多播器的所有应用监听器
* @return a Collection of ApplicationListeners
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener
*/
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners() {
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
return this.defaultRetriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
}
/**
* Return a Collection of ApplicationListeners matching the given
* event type. Non-matching listeners get excluded early.
* 返回给定事件类型的监听器。不匹配的监听将会被尽早剔除。
* @param event the event to be propagated. Allows for excluding
* non-matching listeners early, based on cached matching information.
* 传播的应用事件。基于缓存匹配信息,可以提前剔除不匹配的监听器
* @param eventType the event type 事件类型
* @return a Collection of ApplicationListeners 事件监听器集
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener
*/
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
Object source = event.getSource();//获取事件源
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
//构建事件类型和事件源类型构建监听器缓存key
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// Quick check for existing entry on ConcurrentHashMap...
//从监听器缓存中获取监听缓存key对应的ListenerRetriever
ListenerRetriever retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
//存在,直接返回ListenerRetriever的内部监听器
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
//如果当前bean加载器为null,或者事件类的类加载器为beanClassLoader或其父加载器
//并且事件源类,也是被类加载器为beanClassLoader或其父加载器加载。
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
// Fully synchronized building and caching of a ListenerRetriever
//完全同步创建和缓存
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
//从检索器缓存中获取监听器key对应的监听器检索器ListenerRetriever
retriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
if (retriever != null) {
//缓存中,存在对应的监听器检索器,直接返回相应的监听器集
return retriever.getApplicationListeners();
}
//否则创建监听器检索器
retriever = new ListenerRetriever(true);
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners =
retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, retriever);
//将监听器key与其关联的监听器添加到检索器缓存
this.retrieverCache.put(cacheKey, retriever);
return listeners;
}
}
else {
// No ListenerRetriever caching -> no synchronization necessary
//不需要监听检索器缓存,不需要安全同步
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, null);
}
}
/**
* Actually retrieve the application listeners for the given event and source type.
* @param eventType the event type
* @param sourceType the event source type
* @param retriever the ListenerRetriever, if supposed to populate one (for caching purposes)
* @return the pre-filtered list of application listeners for the given event and source type
*/
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, Class<?> sourceType, ListenerRetriever retriever) {
LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new LinkedList<ApplicationListener<?>>();
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
//获取注册到多播器的监听器
synchronized (this.retrievalMutex) {
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationListener<?>>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
}
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) {
//如果监听器关闭事件源类型sourceType的事件eventType,则添加
//监听器到监听检索器
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
retriever.applicationListeners.add(listener);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
if (!listenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
BeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeans) {
try {
//从bean工厂获取listenerBeanName对应的bean实例
Class<?> listenerType = beanFactory.getType(listenerBeanName);
//如果监听器关闭事件eventType
if (listenerType == null || supportsEvent(listenerType, eventType)) {
//获取listenerBeanName对应的监听器
ApplicationListener<?> listener =
beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
//如果监听器不在当前监听器集中,且关注事件源类型sourceType的事件eventType
if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
//添加监听器到结果集,如果需要添加监听器bean name到监听检索器
if (retriever != null) {
retriever.applicationListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Singleton listener instance (without backing bean definition) disappeared -
// probably in the middle of the destruction phase
}
}
}
//根据监听器的Order或Priority注解值排序监听器
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
return allListeners;
}
/**
* Filter a listener early through checking its generically declared event
* type before trying to instantiate it.
* 在尝试实例监听器之前,通过检查监听器的泛型声明事件类型,尽早地过滤监听器。
* <p>If this method returns {@code true} for a given listener as a first pass,
* the listener instance will get retrieved and fully evaluated through a
* {@link #supportsEvent(ApplicationListener,ResolvableType, Class)} call afterwards.
* 如果此方法返回true,第一个通过的监听器实例将会被检索,然后,
* 通supportsEvent(ApplicationListener,ResolvableType, Class)方法重新完全评估。
* @param listenerType the listener's type as determined by the BeanFactory
* @param eventType the event type to check
* @return whether the given listener should be included in the candidates
* for the given event type
*/
protected boolean supportsEvent(Class<?> listenerType, ResolvableType eventType) {
//如果监听器为GenericApplicationListener和SmartApplicationListener,直接返回true
if (GenericApplicationListener.class.isAssignableFrom(listenerType) ||
SmartApplicationListener.class.isAssignableFrom(listenerType)) {
return true;
}
//获取监听器类型的泛型参数类型
ResolvableType declaredEventType = GenericApplicationListenerAdapter.resolveDeclaredEventType(listenerType);
//如果泛型参数类型为null,或泛型参数为事件类型eventType,则监听器支持事件类型eventType
return (declaredEventType == null || declaredEventType.isAssignableFrom(eventType));
}
/**
* Determine whether the given listener supports the given event.
* 判断给定的监听器是否支持给定的事件
* <p>The default implementation detects the {@link SmartApplicationListener}
* and {@link GenericApplicationListener} interfaces. In case of a standard
* {@link ApplicationListener}, a {@link GenericApplicationListenerAdapter}
* will be used to introspect the generically declared type of the target listener.
* 默认实现将会探测SmartApplicationListener和GenericApplicationListener接口。
* 在标准应用监听器的情况下,GenericApplicationListenerAdapter将用于探测目标的泛型声明类型。
* @param listener the target listener to check
* @param eventType the event type to check against
* @param sourceType the source type to check against
* @return whether the given listener should be included in the candidates
* for the given event type
*/
protected boolean supportsEvent(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ResolvableType eventType, Class<?> sourceType) {
//转换静听器实例为泛型应用监听器GenericApplicationListener
GenericApplicationListener smartListener = (listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener ?
(GenericApplicationListener) listener : new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener));
//通过泛型应用监听器来进一步判断是否支持sourceType事件源发布的事件类型eventType
return (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType) && smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType));
}
从上面可看出,抽象应用事件多播器除了管理监听器相关的实现此外,提供了获取注册到多播器监听器的方法,实际为ListenerRetriever整合 内部监听器集和监听器bean name对应的监听器;同时还有获取给定事件类型的对应的监听器,即关注给定事件类型的监听器,这过程首先从监听器缓存 中获取事件相关的监听器,如果存在,则从监听器检索器中检索出关闭事件的监听器,并封装在监听器检索器ListenerRetriever中,然后添加到监听器缓存中。 监听器缓存键ListenerCacheKey为事件类型与事件源的封装。
我们来小节一下:
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster内部有一个存放监听器的集合 ListenerRetriever,事件监听器缓存retrieverCache(ConcurrentHashMap<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever>)用于存放应用事件与监听器映射关系,bean类加载器 ClassLoader,所属bean工厂BeanFactory 用于获取监听器bean name对应的监听器。所有的监听器注册操作实际由 ListenerRetriever 来完成,ListenerRetriever 使用LinkedHashSet来管理监听器。注意在每次添加和移除监听器之后,将会清除监听器缓存。抽象应用事件多播器除了管理监听器相关的实现此外,提供了获取注册到多播器监听器的方法,实际为ListenerRetriever整合 内部监听器集和监听器bean name对应的监听器;同时还有获取给定事件类型的对应的监听器,即关注给定事件类型的监听器,这过程首先从监听器缓存 中获取事件相关的监听器,如果存在,则从监听器检索器中检索出关闭事件的监听器,并封装在监听器检索器ListenerRetriever中,然后添加到监听器缓存中。 监听器缓存键ListenerCacheKey为事件类型与事件源的封装。
我们回到SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
package org.springframework.context.event;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
import org.springframework.util.ErrorHandler;
/**
* Simple implementation of the {@link ApplicationEventMulticaster} interface.
*SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster实现了应用事件多播器接口。
* <p>Multicasts all events to all registered listeners, leaving it up to
* the listeners to ignore events that they are not interested in.
* Listeners will usually perform corresponding {@code instanceof}
* checks on the passed-in event object.
*多播所有事件到注册监听器,通知监听器关注的事件,忽略掉不相关事件。
* <p>By default, all listeners are invoked in the calling thread.
* This allows the danger of a rogue listener blocking the entire application,
* but adds minimal overhead. Specify an alternative task executor to have
* listeners executed in different threads, for example from a thread pool.
* 默认情况下,所有监听器的调用发生在调用线程中。这样将会阻塞全部应用,但是会减少负载。
* 当前,可以选择使用任务执行器,在不同的线程中执行监听器,比如线程池。
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @see #setTaskExecutor
*/
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster extends AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster {
private Executor taskExecutor;//任务执行器
private ErrorHandler errorHandler;//错误处理器
/**
* Create a new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.
*/
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster() {
}
/**
* Create a new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster for the given BeanFactory.
* 根据给定的bean工厂创建SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
*/
public SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
/**
* Set a custom executor (typically a {@link org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor})
* to invoke each listener with.
* 设置多播器的任务执行器TaskExecutor,用于执行通知监听器相关事件。
* <p>Default is equivalent to {@link org.springframework.core.task.SyncTaskExecutor},
* executing all listeners synchronously in the calling thread.
* 默认等效于SyncTaskExecutor在调用线程内同步执行所有监听器。
* <p>Consider specifying an asynchronous task executor here to not block the
* caller until all listeners have been executed. However, note that asynchronous
* execution will not participate in the caller's thread context (class loader,
* transaction association) unless the TaskExecutor explicitly supports this.
* 考虑到异步任务执行器不会阻塞调用者,直到所有监听器被执行完。然而,除非任务执行器显示
* 地支持,否则异步执行器将不会参加调用线程上下文(类加载器,关联事务)。
* @see org.springframework.core.task.SyncTaskExecutor
* @see org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor
*/
public void setTaskExecutor(Executor taskExecutor) {
this.taskExecutor = taskExecutor;
}
/**
* Return the current task executor for this multicaster.
*/
protected Executor getTaskExecutor() {
return this.taskExecutor;
}
/**
* Set the {@link ErrorHandler} to invoke in case an exception is thrown
* from a listener.
* 设置处理监听器排除的异常的错误处理器。
* <p>Default is none, with a listener exception stopping the current
* multicast and getting propagated to the publisher of the current event.
* If a {@linkplain #setTaskExecutor task executor} is specified, each
* individual listener exception will get propagated to the executor but
* won't necessarily stop execution of other listeners.
* 默认为无,当监听器异常时,将会停止事件多播,并将异常传播给发布事件的调用者。
* 如果设置了任务执行,则每个监听的异常将会传播给执行器,不需要停止器其他监听器
* 的执行。
* <p>Consider setting an {@link ErrorHandler} implementation that catches
* and logs exceptions (a la
* {@link org.springframework.scheduling.support.TaskUtils#LOG_AND_SUPPRESS_ERROR_HANDLER})
* or an implementation that logs exceptions while nevertheless propagating them
* (e.g. {@link org.springframework.scheduling.support.TaskUtils#LOG_AND_PROPAGATE_ERROR_HANDLER}).
* 可以考虑设置异常处理器为捕捉异常,并输出异常日志异常处理器LoggingErrorHandler,也可以为输出异常日志,
* 并重新抛出异常的PropagatingErrorHandler。
* @since 4.1
*/
public void setErrorHandler(ErrorHandler errorHandler) {
this.errorHandler = errorHandler;
}
/**
* Return the current error handler for this multicaster.
* @since 4.1
*/
protected ErrorHandler getErrorHandler() {
return this.errorHandler;
}
/**
* 多播给定的事件
*/
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
/**
* 通知关注事件的所有监听器
*/
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
//获取应用事件的可解决类型eventType
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
//遍历关闭事件的监听器
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();//获取任务执行器
//如果任务执行不为null,则任务执行器通知监听器发生器关注事件,否则在当前线程中完成相关工作
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
});
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
/**
* 获取应用事件可解决类型ResolvableType
* @param event
* @return
*/
private ResolvableType resolveDefaultEventType(ApplicationEvent event) {
return ResolvableType.forInstance(event);
}
/**
* Invoke the given listener with the given event.
* 通知相关监听器,发生其关注事件。
* @param listener the ApplicationListener to invoke
* @param event the current event to propagate
* @since 4.1
*/
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
//如果有异常处理器,则捕捉监听器异常,否则直接通知监听器
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
/**
* @param listener
* @param event
*/
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
//调用监听器处理应用事件操作。
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || msg.startsWith(event.getClass().getName())) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
从上面可以看出,简单事件多播器SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,主要实现了多播器的多播事件操作,即将应用事件传递给相应的应用监听器,非关注 此事件的监听器,将会被忽略。默认情况下,简单事件多播器在当前线程下调用监听器的事件处理器操作,当然我们也可以设置多播器的任务执行器 Executor,委托任务执行器 调用监听器的事件处理器操作,同时我们也可以设置异常处理器 ErrorHandler 用于处理调用监听器过程中异常。
最后我们以SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的类图结束这篇文章。
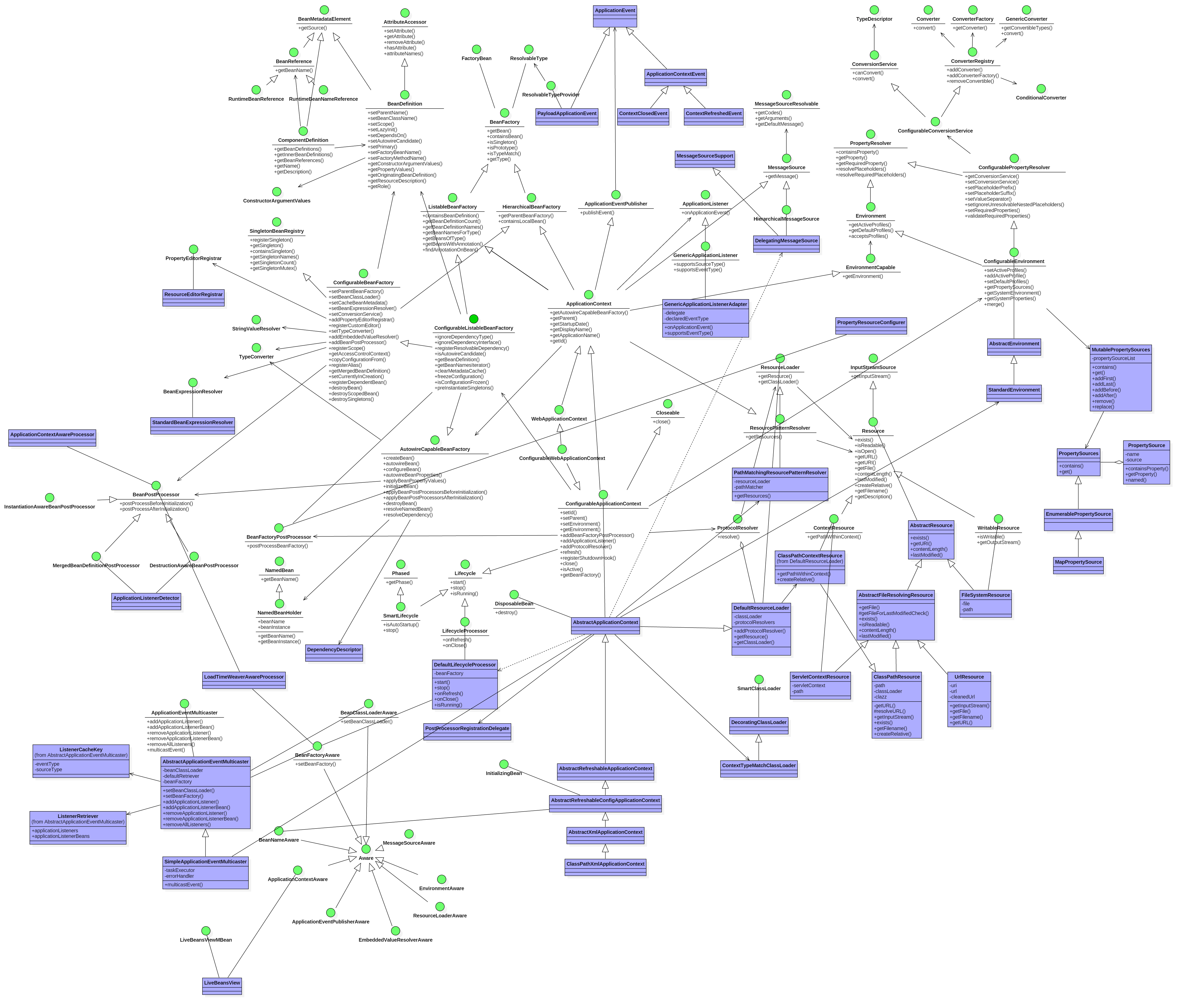
总结
应用事件多播器ApplicationEventMulticaster主要提供了应用事件监听器的管理操作(添加、移除),同时提供了发布应用事件到所管理的应用监听器的操作。 应用事件多播器典型应用,为代理应用上下文,发布相关应用事件。 BeanClassLoaderAware主要体用了设置bean类加载器的操作,主要用于框架实现类想用根据的name获取bean的应用类型的场景。
AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster内部有一个存放监听器的集合 ListenerRetriever,事件监听器缓存retrieverCache(ConcurrentHashMap<ListenerCacheKey, ListenerRetriever>)用于存放应用事件与监听器映射关系,bean类加载器 ClassLoader,所属bean工厂BeanFactory 用于获取监听器bean name对应的监听器。所有的监听器注册操作实际由 ListenerRetriever 来完成,ListenerRetriever 使用LinkedHashSet来管理监听器。注意在每次添加和移除监听器之后,将会清除监听器缓存。抽象应用事件多播器除了管理监听器相关的实现此外,提供了获取注册到多播器监听器的方法,实际为ListenerRetriever整合 内部监听器集和监听器bean name对应的监听器;同时还有获取给定事件类型的对应的监听器,即关注给定事件类型的监听器,这过程首先从监听器缓存 中获取事件相关的监听器,如果存在,则从监听器检索器中检索出关闭事件的监听器,并封装在监听器检索器ListenerRetriever中,然后添加到监听器缓存中。 监听器缓存键ListenerCacheKey为事件类型与事件源的封装。
简单事件多播器SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,主要实现了多播器的多播事件操作,即将应用事件传递给相应的应用监听器,非关注 此事件的监听器,将会被忽略。默认情况下,简单事件多播器在当前线程下调用监听器的事件处理器操作,当然我们也可以设置多播器的任务执行器 Executor,委托任务执行器 调用监听器的事件处理器操作,同时我们也可以设置异常处理器 ErrorHandler 用于处理调用监听器过程中异常。