SpelExpressionParser使用说明
write by valuewithTime, 2020-06-15 16:36官方wiki
中文解析
Spring EL使用
spring-framework-4.3.x
引言
Spring表达式语言(简称SpEl)是一个支持查询和操作运行时对象导航图功能的强大的表达式语言. 它的语法类似于传统EL,但提供额外的功能,最出色的就是函数调用和简单字符串的模板函数。
尽管有其他可选的 Java 表达式语言,如 OGNL, MVEL,JBoss EL 等等,但 Spel 创建的初衷是了给 Spring 社区提供一种简单而高效的表达式语言,一种可贯穿整个 Spring 产品组的语言。这种语言的特性应基于 Spring 产品的需求而设计。
虽然SpEL引擎作为Spring 组合里的表达式解析的基础 ,但它不直接依赖于Spring,可独立使用。为了整合,许多在本章使用SpEL例子就好像它是一个独立的表达式语言。这就需要创建一些引导 如解析器这样的基础构造类。大多数Spring用户将不再需要处理这些基础构建,而是仅将作者表达的字符串进行解析。一个传统的使用例子是集成SpEL去创建XML或者定义Bean的注解,可以选择这里看到 表达式支持定义bean.
本章讲介绍SpEL的API,其语言语法的特点。在几个地方,Inventor和Inventor’s Society 类被用做表达式解析的目标对象 。 这些类声明和使用数据一直贯穿本章结尾。
目录
使用示例
package cn.home.spring;
import cn.home.entity.User;
import cn.home.util.SpelExpressionUtil;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.expression.BeanFactoryResolver;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.EvaluationContext;
import org.springframework.expression.Expression;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.support.StandardEvaluationContext;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @ClassName: TestSpelExpressionParser
* @Description:
* doc
* https://juejin.im/post/5b933fce5188255c402ae50e
* 官方wiki
* https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/3.0.x/reference/expressions.html
* http://itmyhome.com/spring/expressions.html
* @see SpelExpressionUtil
* @Author: Donaldhan
* @Date: 2020-06-16 10:38
*/
@Slf4j
public class TestSpelExpressionParser {
/**
*
*/
@Test
public void testArgrimth(){
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("6+2");
Integer result = (Integer) expression.getValue();
log.info("testArgrimth result:{}", result);
}
/**
*
*/
@Test
public void testString(){
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("'SpEL'.concat(' thinking')");
String result = (String) expression.getValue();
log.info("testString result:{}", result);
}
/**
*
*/
@Test
public void testEntity(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("valuewithTime");
user.setAge(23);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context=new StandardEvaluationContext(user);
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("name");
String result = expression.getValue(context,String.class);
log.info("testEntity result:{}", result);
}
@Test
public void testTypeConversion(){
class Simple {
public List<Boolean> booleanList = new ArrayList<Boolean>();
}
Simple simple = new Simple();
simple.booleanList.add(true);
StandardEvaluationContext simpleContext = new StandardEvaluationContext(simple);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// false is passed in here as a string. SpEL and the conversion service will
// correctly recognize that it needs to be a Boolean and convert it
parser.parseExpression("booleanList[0]").setValue(simpleContext, "false");
// b will be false
Boolean b = simple.booleanList.get(0);
log.info("testTypeConversion result:{}", b);
}
/**
*
*/
@Test
public void testValue(){
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context=new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setVariable("name", "valuewithTime");
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("#name");
String result = expression.getValue(context,String.class);
log.info("testValue result:{}", result);
}
/**
*
*/
@Test
public void testBean(){
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
//Spring 环境下注入
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
StandardEvaluationContext sec = new StandardEvaluationContext(context);
sec.setBeanResolver(new BeanFactoryResolver(context));
// This will end up calling resolve(context,"foo") on BeanFactoryResolver during evaluation
Object bean = parser.parseExpression("@dataSource").getValue(context);
log.info("testBean bean:{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(bean));
}
@Test
public void testBeanProperties(){
@Data
class UserWapper {
User user;
}
User user = new User();
user.setName("valuewithTime");
user.setAge(23);
UserWapper userWapper = new UserWapper();
userWapper.setUser(user);
EvaluationContext context=new StandardEvaluationContext(userWapper);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("user.name");
String result = expression.getValue(context,String.class);
log.info("testBeanProperties result:{}", result);
}
}
解析2种使用方式, 对象属性properties,变量;
先来看对象属性properties表达式。
对象属性properties表达式
对象属性properties表达式属性使用方式有如下两种方式;
直接引用对象属性
/**
*
*/
@Test
public void testEntity(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("valuewithTime");
user.setAge(23);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context=new StandardEvaluationContext(user);
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("name");
String result = expression.getValue(context,String.class);
log.info("testEntity result:{}", result);
}
引用对象的属性对象属性
@Test
public void testBeanProperties(){
@Data
class UserWapper {
User user;
}
User user = new User();
user.setName("valuewithTime");
user.setAge(23);
UserWapper userWapper = new UserWapper();
userWapper.setUser(user);
EvaluationContext context=new StandardEvaluationContext(userWapper);
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("user.name");
String result = expression.getValue(context,String.class);
log.info("testBeanProperties result:{}", result);
}
先来看一下构造标准评估上下文StandardEvaluationContext
/**
* Create a {@code StandardEvaluationContext} with the given root object.
* @param rootObject the root object to use
* @see #setRootObject
*/
public StandardEvaluationContext(Object rootObject) {
this.rootObject = new TypedValue(rootObject);
}
public class StandardEvaluationContext implements EvaluationContext {
private TypedValue rootObject;//根对象
private List<ConstructorResolver> constructorResolvers;//构造解决器
private List<MethodResolver> methodResolvers;//方法解决器
private BeanResolver beanResolver;//bean解决器
private ReflectiveMethodResolver reflectiveMethodResolver;//反射方法解决器
private List<PropertyAccessor> propertyAccessors;//属性访问器
private TypeLocator typeLocator;//类型定位器
private TypeConverter typeConverter;//类型转化器
private TypeComparator typeComparator = new StandardTypeComparator();//类型比较器
private OperatorOverloader operatorOverloader = new StandardOperatorOverloader();//计算操作器
private final Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String, Object>();//求值表达式上下文变量
...
}
/**
* Encapsulates an object and a {@link TypeDescriptor} that describes it.
* The type descriptor can contain generic declarations that would not
* be accessible through a simple {@code getClass()} call on the object.
*封装了对象和其类型描述。类型描述可以包含泛型声明,但不能够通过{@code getClass()}方法调用
*访问。
* @author Andy Clement
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.0
*/
public class TypedValue {
public static final TypedValue NULL = new TypedValue(null);
private final Object value;
private TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor;
...
}
SpelExpressionParser解析器
/**
* SpEL parser. Instances are reusable and thread-safe.
*SpEL解析器,实例可以重用,且线程安全。
* @author Andy Clement
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.0
*/
public class SpelExpressionParser extends TemplateAwareExpressionParser {
private final SpelParserConfiguration configuration;//解析器配置
...
}
public abstract class TemplateAwareExpressionParser implements ExpressionParser {
/**
* Default ParserContext instance for non-template expressions.
*/
private static final ParserContext NON_TEMPLATE_PARSER_CONTEXT = new ParserContext() {
@Override
public String getExpressionPrefix() {
return null;
}
@Override
public String getExpressionSuffix() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isTemplate() {
return false;
}
};
@Override
public Expression parseExpression(String expressionString) throws ParseException {
return parseExpression(expressionString, NON_TEMPLATE_PARSER_CONTEXT);
}
@Override
public Expression parseExpression(String expressionString, ParserContext context) throws ParseException {
if (context == null) {
context = NON_TEMPLATE_PARSER_CONTEXT;
}
if (context.isTemplate()) {
return parseTemplate(expressionString, context);
}
else {
return doParseExpression(expressionString, context);
}
}
...
}
//SpelExpressionParser
@Override
protected SpelExpression doParseExpression(String expressionString, ParserContext context) throws ParseException {
return new InternalSpelExpressionParser(this.configuration).doParseExpression(expressionString, context);
}
//InternalSpelExpressionParser
protected SpelExpression doParseExpression(String expressionString, ParserContext context) throws ParseException {
try {
this.expressionString = expressionString;
Tokenizer tokenizer = new Tokenizer(expressionString);
this.tokenStream = tokenizer.process();
this.tokenStreamLength = this.tokenStream.size();
this.tokenStreamPointer = 0;
this.constructedNodes.clear();
SpelNodeImpl ast = eatExpression();
if (moreTokens()) {
throw new SpelParseException(peekToken().startPos, SpelMessage.MORE_INPUT, toString(nextToken()));
}
Assert.isTrue(this.constructedNodes.isEmpty(), "At least one node expected");
return new SpelExpression(expressionString, ast, this.configuration);
}
catch (InternalParseException ex) {
throw ex.getCause();
}
}
//
/**
* 解析el表达式
* @return
*/
public List<Token> process() {
while (this.pos < this.max) {
char ch = this.charsToProcess[this.pos];
if (isAlphabetic(ch)) {
lexIdentifier();
}
else {
switch (ch) {
case '+':
if (isTwoCharToken(TokenKind.INC)) {
pushPairToken(TokenKind.INC);
}
else {
pushCharToken(TokenKind.PLUS);
}
break;
case '_': // the other way to start an identifier
lexIdentifier();
break;
case '-':
if (isTwoCharToken(TokenKind.DEC)) {
pushPairToken(TokenKind.DEC);
}
else {
pushCharToken(TokenKind.MINUS);
}
break;
case ':':
pushCharToken(TokenKind.COLON);
break;
case '.':
pushCharToken(TokenKind.DOT);
break;
...
}
//SpelExpression
/**
* A {@code SpelExpression} represents a parsed (valid) expression that is ready to be
* evaluated in a specified context. An expression can be evaluated standalone or in a
* specified context. During expression evaluation the context may be asked to resolve
* references to types, beans, properties, and methods.
* 准备根据给定的上下文解析的el表示。一个表达式通过单独的或者一个特殊的上下文进行评估。使用上下文评估对应的类型
* bean,属性,和方法
* ,
* @author Andy Clement
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.0
*/
public class SpelExpression implements Expression {
// Number of times to interpret an expression before compiling it
private static final int INTERPRETED_COUNT_THRESHOLD = 100;
// Number of times to try compiling an expression before giving up
private static final int FAILED_ATTEMPTS_THRESHOLD = 100;
/**
* 表达式
*/
private final String expression;
/**
* el抽象预发树
*/
private final SpelNodeImpl ast;
private final SpelParserConfiguration configuration;
...
}
从给定的评估上下文获取给定类型的表示是的值
//SpelExpression
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <T> T getValue(EvaluationContext context, Class<T> expectedResultType) throws EvaluationException {
Assert.notNull(context, "EvaluationContext is required");
if (this.compiledAst != null) {
try {
TypedValue contextRoot = context.getRootObject();
Object result = this.compiledAst.getValue(contextRoot.getValue(), context);
if (expectedResultType != null) {
return ExpressionUtils.convertTypedValue(context, new TypedValue(result), expectedResultType);
}
else {
return (T) result;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// If running in mixed mode, revert to interpreted
if (this.configuration.getCompilerMode() == SpelCompilerMode.MIXED) {
this.interpretedCount = 0;
this.compiledAst = null;
}
else {
// Running in SpelCompilerMode.immediate mode - propagate exception to caller
throw new SpelEvaluationException(ex, SpelMessage.EXCEPTION_RUNNING_COMPILED_EXPRESSION);
}
}
}
//根据评估上下文,跟对象的类型,及配置构造状态表达式
ExpressionState expressionState = new ExpressionState(context, this.configuration);
TypedValue typedResultValue = this.ast.getTypedValue(expressionState);
//编译检查
checkCompile(expressionState);
//
return ExpressionUtils.convertTypedValue(context, typedResultValue, expectedResultType);
}
//ExpressionUtils
public static <T> T convertTypedValue(EvaluationContext context, TypedValue typedValue, Class<T> targetType) {
Object value = typedValue.getValue();
if (targetType == null) {
return (T) value;
}
if (context != null) {
return (T) context.getTypeConverter().convertValue(
value, typedValue.getTypeDescriptor(), TypeDescriptor.valueOf(targetType));
}
if (ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(targetType, value)) {
return (T) value;
}
throw new EvaluationException("Cannot convert value '" + value + "' to type '" + targetType.getName() + "'");
}
//StandardTypeConverter
@Override
public Object convertValue(Object value, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
try {
return this.conversionService.convert(value, sourceType, targetType);
}
catch (ConversionException ex) {
throw new SpelEvaluationException(ex, SpelMessage.TYPE_CONVERSION_ERROR,
(sourceType != null ? sourceType.toString() : (value != null ? value.getClass().getName() : "null")),
targetType.toString());
}
}
//StandardTypeConverter
/**
* Create a StandardTypeConverter for the default ConversionService.
*/
public StandardTypeConverter() {
this.conversionService = DefaultConversionService.getSharedInstance();
}
//DefaultConversionService
/**
* Create a new {@code DefaultConversionService} with the set of
* {@linkplain DefaultConversionService#addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry) default converters}.
* 根据默认的转换器集,创建一个默认转换器实例
*/
public DefaultConversionService() {
addDefaultConverters(this);
}
/**
* Add converters appropriate for most environments.
* 添加大多数环境使用的转化器
* @param converterRegistry the registry of converters to add to
* (must also be castable to ConversionService, e.g. being a {@link ConfigurableConversionService})
* @throws ClassCastException if the given ConverterRegistry could not be cast to a ConversionService
*/
public static void addDefaultConverters(ConverterRegistry converterRegistry) {
addScalarConverters(converterRegistry);
addCollectionConverters(converterRegistry);
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ByteBufferConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
if (jsr310Available) {
Jsr310ConverterRegistrar.registerJsr310Converters(converterRegistry);
}
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToObjectConverter());
converterRegistry.addConverter(new IdToEntityConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
converterRegistry.addConverter(new FallbackObjectToStringConverter());
if (javaUtilOptionalClassAvailable) {
converterRegistry.addConverter(new ObjectToOptionalConverter((ConversionService) converterRegistry));
}
}
//ObjectToObjectConverter
@Override
public Object convert(Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
if (source == null) {
return null;
}
Class<?> sourceClass = sourceType.getType();
Class<?> targetClass = targetType.getType();
//从目标类,获取元类型的成员
Member member = getValidatedMember(targetClass, sourceClass);
try {
if (member instanceof Method) {
//对应方法
Method method = (Method) member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
if (!Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
return method.invoke(source);
}
else {
return method.invoke(null, source);
}
}
else if (member instanceof Constructor) {
//构造函数
Constructor<?> ctor = (Constructor<?>) member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
return ctor.newInstance(source);
}
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new ConversionFailedException(sourceType, targetType, source, ex.getTargetException());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new ConversionFailedException(sourceType, targetType, source, ex);
}
// If sourceClass is Number and targetClass is Integer, the following message should expand to:
// No toInteger() method exists on java.lang.Number, and no static valueOf/of/from(java.lang.Number)
// method or Integer(java.lang.Number) constructor exists on java.lang.Integer.
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format("No to%3$s() method exists on %1$s, " +
"and no static valueOf/of/from(%1$s) method or %3$s(%1$s) constructor exists on %2$s.",
sourceClass.getName(), targetClass.getName(), targetClass.getSimpleName()));
}
直接从表示是获取对应的值
@Override
public Object getValue() throws EvaluationException {
if (this.compiledAst != null) {
try {
TypedValue contextRoot =
(this.evaluationContext != null ? this.evaluationContext.getRootObject() : null);
return this.compiledAst.getValue(
(contextRoot != null ? contextRoot.getValue() : null), this.evaluationContext);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// If running in mixed mode, revert to interpreted
if (this.configuration.getCompilerMode() == SpelCompilerMode.MIXED) {
this.interpretedCount = 0;
this.compiledAst = null;
}
else {
// Running in SpelCompilerMode.immediate mode - propagate exception to caller
throw new SpelEvaluationException(ex, SpelMessage.EXCEPTION_RUNNING_COMPILED_EXPRESSION);
}
}
}
//根据评估上下文和配置构造表达式状态
ExpressionState expressionState = new ExpressionState(getEvaluationContext(), this.configuration);
//从抽象语法树获取表达式的值
Object result = this.ast.getValue(expressionState);
checkCompile(expressionState);
return result;
}
想知道,具体可以调试, 我们来调试跟踪一下:
跟踪调试
InternalSpelExpressionParser解析表达式生成抽象语法树
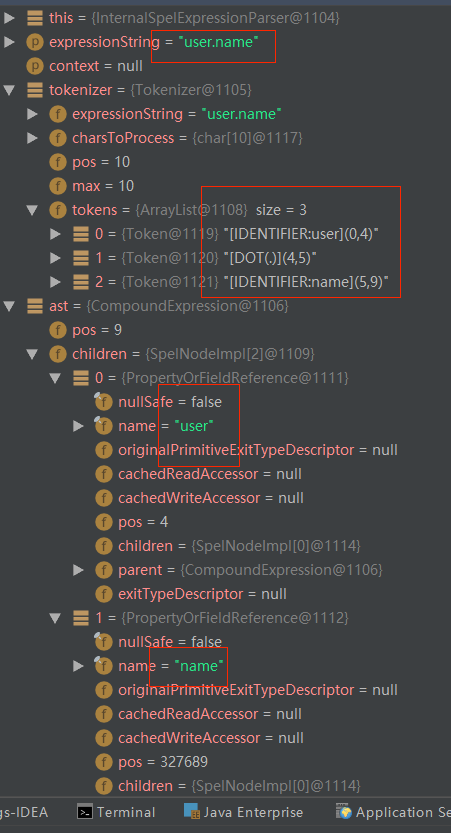
从上图可以看出,生成的抽象语法树有两个节点一个为user,一个为name;
再来看一下如何获取属性值 //SpelExpression
public <T> T getValue(EvaluationContext context, @Nullable Class<T> expectedResultType) throws EvaluationException {
Assert.notNull(context, "EvaluationContext is required");
...
ExpressionState expressionState = new ExpressionState(context, this.configuration);
TypedValue typedResultValue = this.ast.getTypedValue(expressionState);
checkCompile(expressionState);
return ExpressionUtils.convertTypedValue(context, typedResultValue, expectedResultType);
}
//SpelNodeImpl
@Override
public final TypedValue getTypedValue(ExpressionState expressionState) throws EvaluationException {
return getValueInternal(expressionState);
}
注意这里是一个递归调用。
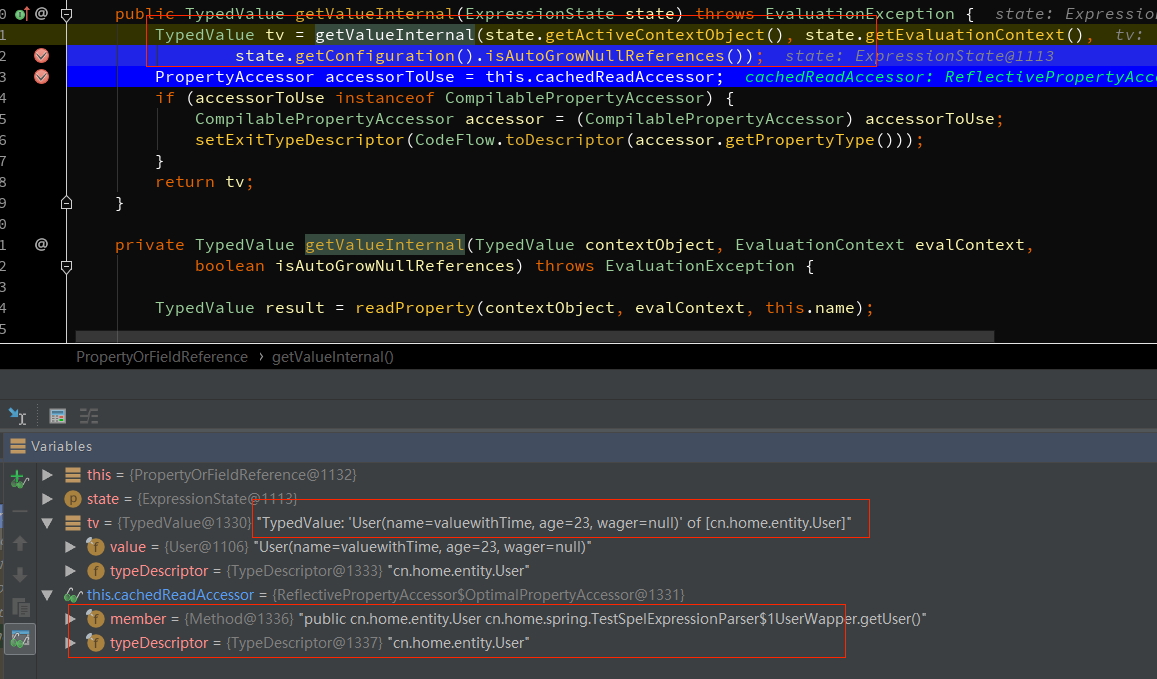
获取内部值的结果user属性对应的TypeVlaue为User, 往里走解析属性对应的值
//PropertyOrFieldReference(SpelNodeImpl)
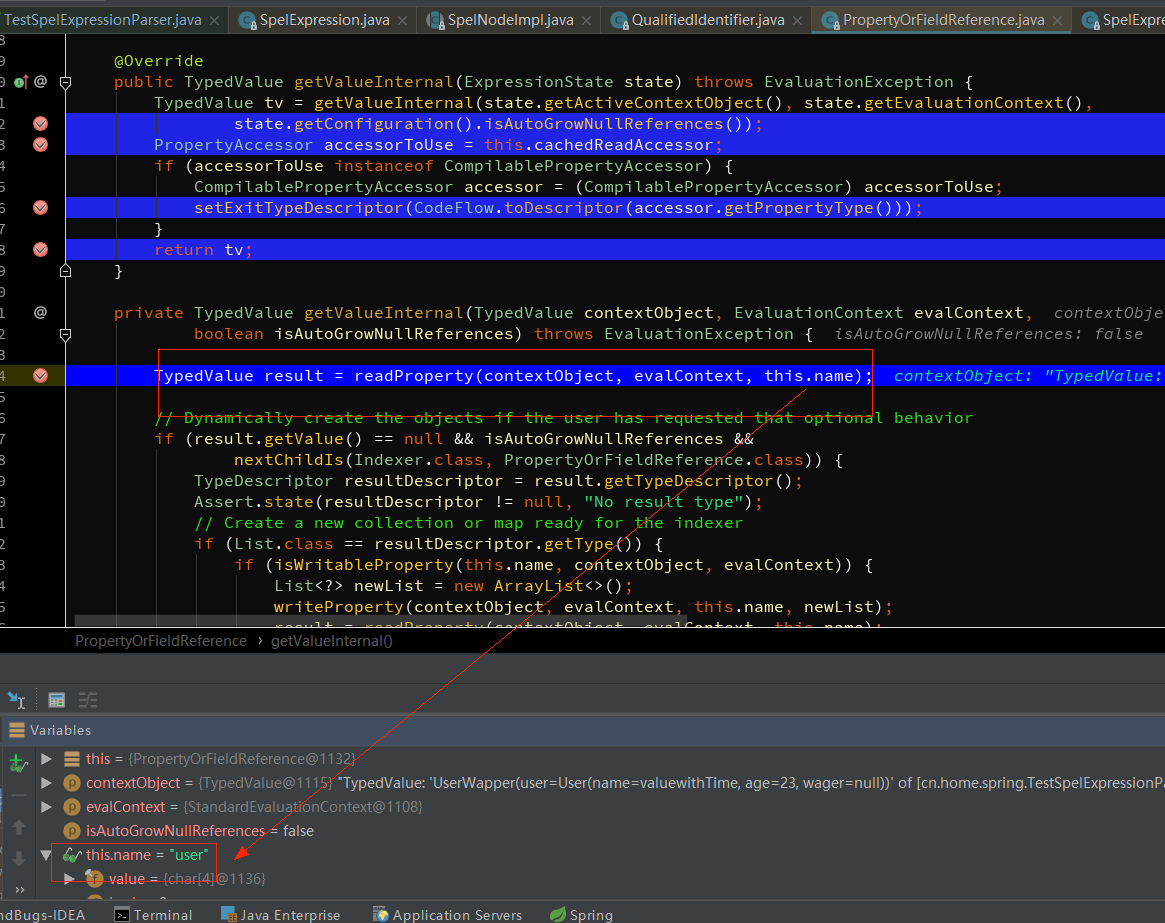
递归调试,解析name的值
//PropertyOrFieldReference(SpelNodeImpl)
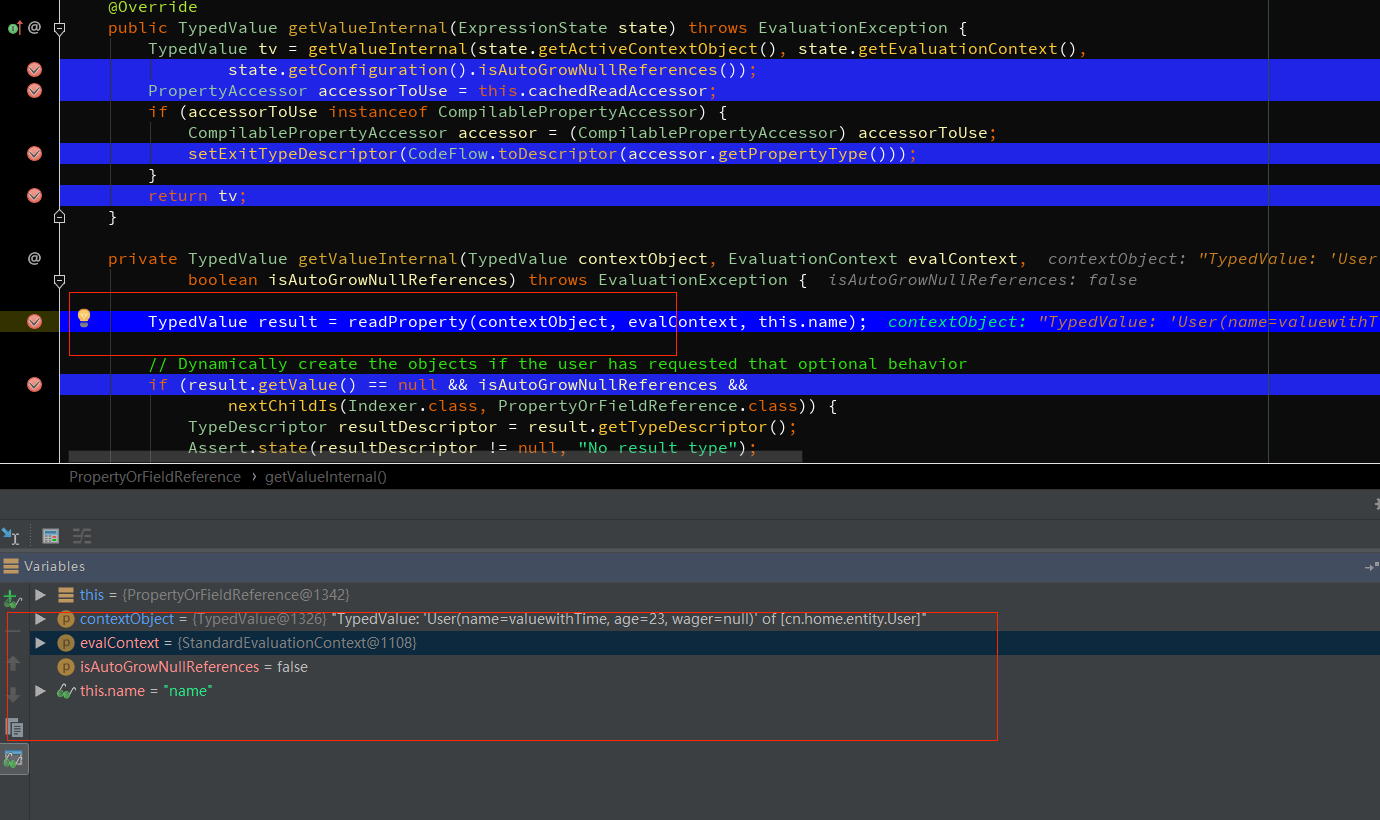
//SpelExpression
跳出递归,返回解析值为Type
变量表达式
/**
*
*/
@Test
public void testValue(){
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
EvaluationContext context=new StandardEvaluationContext();
context.setVariable("name", "valuewithTime");
Expression expression = parser.parseExpression("#name");
String result = expression.getValue(context,String.class);
log.info("testValue result:{}", result);
}
原理同上。
总结
属性el表达式,首先解析表达,生成对应的抽象语法树,语法树的节点为SpelNodeImpl, 针对属性表达式,对应的节点类型为PropertyOrFieldReference。获取表达式值使用时通过表达式队对应的具体节点类型。PropertyOrFieldReference主要通过反射获取对应标准评估上下文绑定的RootObject的属性。