AbstractApplicationContext源码解析第五讲
write by donaldhan, 2018-01-26 13:25引言
我们可以通过setEnvironment配置上下文环境,通过getEnvironment获取上下文位置,如果没有则上下文的环境默认为StandardEnvironment。 需要注意的是在修改应用上下文环境操作,应该在刷新上下文refresh操作之前。
获取自动装配bean工厂AutowireCapableBeanFactory,实际委托给获取bean工厂方法getBeanFactory,getBeanFactory方法待子类扩展。
抽象应用上下文发布应用事件实际委托给内部的应用事件多播器,应用事件多播器在上下文刷新的时候初始化,如果配置有应用事件多播器 ,则使用配置的应用事件多播器发布应用事件,否则默认使用SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster。在发布应用事件的时候,如果预发布事件集不为空, 则发布事件集中的应用事件,如果当上下文的父上下文不为空,则调用父上下文的事件发布操作,将事件传播给父上下文中的应用监听器。
在设置上下文的父应用上文时,如果父上下文的环境配置为可配置环境,则合并父上下文环境到当前上下文环境。
添加bean工厂后处理器,实际为将bean工厂后处理器添加到上下文的bean工厂后处理器集中beanFactoryPostProcessors(ArrayList
应用上下文刷新的过程为:
-
准备上下文刷新操作; 准备上下文刷新操作主要初始化应用上下文环境中的占位符属性源,验证所有需要可解决的标注属性,创建预发布应用事件集earlyApplicationEvents(LinkedHashSet
)。 初始化属性源方法 *#initPropertySources* 待子类实现。 -
告诉子类刷新内部bean工厂; 通知子类刷新内部bean工厂实际操作在 #refreshBeanFactory 中,刷新bean工厂操作待子类扩展,在刷新完bean工厂之后,返回当前上下文的bean工厂, 返回当前上下文的bean工厂 #getBeanFactory 待子类实现。
-
准备上下文使用的bean工厂; 预备bean工厂畅主要的是设置工厂类加载器,Spring EL表达式解决器 StandardBeanExpressionResolver,资源编辑器 ResourceEditorRegistrar; 添加bean后处理器 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 处理与应用上下文关联的Awarebean实例,比如 EnvironmentAware,EmbeddedValueResolverAware,ResourceLoaderAware ApplicationEventPublisherAware,MessageSourceAware,ApplicationContextAware,并忽略掉这些依赖。同时注册 BeanFactory,ResourceLoader,ApplicationEventPublisher, ApplicationContext 类到工厂可解决类。添加应用监听器探测器,探测应用监听器bean定义,并添加到应用上下文中。如果bean工厂中包含加载时间织入器,则设置加载时间织入器后处理器 LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor , 并配置类型匹配的临时类加载器。最后如果需要,注册环境,系统属性,系统变量单例bean到bean工厂。
-
在上下文子类中,允许后处理bean工厂; 在标准初始化完成后,修改应用上下文内部的bean工厂。所有的bean定义已经加载,但是还没bean已完成初始化。 允许在确定的应用上下文实现中注册特殊的bean后处理器。方法postProcessBeanFactory待子类扩展。
-
调用注册到上下文中的工厂后处理器; 这一步所有的做的事情为调用bean工厂后处理器,处理bean工厂,具体过程为:如果为bean工厂为bean定义注册器实例, 则调用上下文中的bean定义注册器后处理器,处理工厂,然后调用实现了PriorityOrdered,Ordered接口和剩余的bean定义注册器后处理器,处理bean工厂; 如果bean工厂不是bean定义注册器实例,则使用上下文中的bean工厂后处理器,处理bean工厂。从bean工厂内获取所有bean工厂处理器实例, 按实现了PriorityOrdered,Ordered接口和剩余的bean工厂后处理器顺序,处理bean工厂;最后清空bean工厂的元数据缓存。 如果bean工厂的临时加载器为空,且包含加载时间织入器,则设置bean工厂的加载时间织入器后处理器,设置bean工厂的临时类加载器为[ContextTypeMatchClassLoader][]。
-
注册拦截bean创建的bean后处理器; 注册bean工厂的bean后处理操作,主要委托给[PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate][],注册过程为: 注册实现PriorityOrdered,Ordered和剩余的bean后处理器到bean工厂,然后注册内部bean后处理器[MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor][]; 最后添加应用监听器探测器[ApplicationListenerDetector][]。
-
初始化上下文的消息源; 如果bean工厂包含消息源,则配置为上下文消息源,如果当前上下文父上下文不为空且消息源为层级消息源HierarchicalMessageSource, 配置当前消息源的父消息源为当前上下文内部父消息源。否则创建上下文内部的父消息源的代理DelegatingMessageSource,并注册消息源到bean工厂。
-
始化上下文的事件多播器; 初始化上下文的事件多播器过程为,如果bean工厂包含应用事件多播器,则配置应用上下文的应用事件多播器为bean工厂内的应用事件多播器; 否则使用SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,并注册到bean工厂。
-
初始化上下文子类中的其他特殊的bean; 初始化上下文子类中的其他特殊的bean方法onRefresh,待子类扩展使用。
-
检查监听器bean,并注册; 注册监听器过程,主要是注册应用上下文中的应用监听器到应用事件多播器,注册bean工厂内部的应用监听器 到应用事件多播器,如果存在预发布应用事件,则多播应用事件。
-
初始化所有遗留的非懒加载单例bean; 完成上下文bean工厂的初始化,初始化所有遗留的单例bean,如果bean工厂内存在转换服务ConversionService,则配置bean工厂的转换服务; 如果没有bean后处理器(PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer)注册,则注册一个默认的嵌入式值解决器StringValueResolver,主要解决注解属性的值; 初始化先前加载时间织入器Aware bean,允许注册他们的变换器;停止使用临时类加载器用于类型匹配;冻结bean工厂配置;最后初始化所有剩余的单例bean。
-
完成上下文刷新; 完成上下文刷新主要所有的工作为,初始化上下文的生命周期处理器,默认为 DefaultLifecycleProcessor,生命周期处理器主要管理 bean工厂内部的生命周期bean。然后启动bean工厂内的生命周期bean。然后发布上下文刷新事件给应用监听器,最后注册上下文到LiveBeansView MBean, 以便监控上下文中bean工厂内部的bean的定义及依赖。 如果以上过程出现异常则执行13,14步:
-
销毁已经创建的单例bean,避免资源空占; 销毁bean操作,主要委托给应用上文的内部bean工厂,bean工厂完成销毁所有的单例bean。
-
重置上下文激活状态标志; 最后执行15步,
-
由于我们不在需要单例bean的元数据,重置Spring核心的一般内省缓存。 主要清除,类的方法与属性缓存,可解决类型缓存,及类缓存。
这是我们上一篇文章AbstractApplicationContext源码解析第四讲所讲的内容,主要的是应用上下文的刷新操作,今天我们来看抽象应用上下文的剩余操作,主要是关闭上下文,bean工厂,消息源,及资源相关的操作。
目录
AbstractApplicationContext定义
源码参见:AbstractApplicationContext
注册虚拟机关闭Hook
先来看注册虚拟机关闭Hook
/**
* Register a shutdown hook with the JVM runtime, closing this context
* on JVM shutdown unless it has already been closed at that time.
* <p>Delegates to {@code doClose()} for the actual closing procedure.
* 注册虚拟机运行时关闭Hook,除非上下文在虚拟机关闭时已经关闭,否则关闭上下文。代理{@code doClose()}方法,
* 完成实际的关闭过程。
* @see Runtime#addShutdownHook
* @see #close()
* @see #doClose()
*/
@Override
public void registerShutdownHook() {
if (this.shutdownHook == null) {
// No shutdown hook registered yet.
this.shutdownHook = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (startupShutdownMonitor) {
doClose();
}
}
};
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);
}
}
关键在Hook线程任务:
/**
* Actually performs context closing: publishes a ContextClosedEvent and
* destroys the singletons in the bean factory of this application context.
* <p>Called by both {@code close()} and a JVM shutdown hook, if any.
* 执行实际的关闭上下文:发布上下文关闭事件ContextClosedEvent,销毁应用上下文中的bean工厂内的单例bean。
* 如果需要,可以通过{@code close()}方法和添加虚拟机Hook调用。
* @see org.springframework.context.event.ContextClosedEvent
* @see #destroyBeans()
* @see #close()
* @see #registerShutdownHook()
*/
protected void doClose() {
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Closing " + this);
}
//从bean视图中移除上下文
LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this);
try {
// Publish shutdown event.发布关闭事件
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);
}
// Stop all Lifecycle beans, to avoid delays during individual destruction.
//停止所有生命周期bean,以避免在个人析构过程中的延迟。
if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) {
try {
this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", ex);
}
}
// Destroy all cached singletons in the context's BeanFactory.
//销毁上下文bean工厂中所有缓存的单例bean。
destroyBeans();
// Close the state of this context itself.
//关闭上下文状态
closeBeanFactory();
// Let subclasses do some final clean-up if they wish...
//如果希望,可以让子类做一些其他清除工作。
onClose();
//更新上下文激活状态为false。
this.active.set(false);
}
}
/**
* Subclasses must implement this method to release their internal bean factory.
* 子类必须实现此方法已释放工厂的内部bean。
* This method gets invoked by {@link #close()} after all other shutdown work.
* <p>Should never throw an exception but rather log shutdown failures.
* 此方法在所有其他关闭工作后,通过{@link #close()}方法调用。应该不要抛出异常,而是日志输出关闭失败信息。
*/
protected abstract void closeBeanFactory();
/**
* Template method which can be overridden to add context-specific shutdown work.
* The default implementation is empty.
* 此方法为模板方法,可以重写添加上下文特殊的关闭工作,默认实现为空。
* <p>Called at the end of {@link #doClose}'s shutdown procedure, after
* this context's BeanFactory has been closed. If custom shutdown logic
* needs to execute while the BeanFactory is still active, override
* the {@link #destroyBeans()} method instead.
* 在bean工厂上下文已经关闭,即{@link #doClose}关闭过程末端,调用此方法。当bean工厂处于激活状态,
* 如果需要定制一些关闭逻辑,可以重写{@link #destroyBeans()} 方法。
*/
protected void onClose() {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
从上面可以看出,注册虚拟机关闭Hook,委托给运行时Runtime,而hook线程完成实际工作为,从LiveBeansView反注册当前应用上下文, 发布上下文关闭事件ContextClosedEvent,销毁上下文bean工厂中所有缓存的单例bean,关闭上下文状态closeBeanFactory,如果希望, 可以让子类做一些其他清除工作onClose;closeBeanFactory和onClose方法待子类扩展。
关闭销毁应用上下文
/**
* DisposableBean callback for destruction of this instance.
* 析构当前工厂实例的DisposableBean回调。
* <p>The {@link #close()} method is the native way to shut down
* an ApplicationContext, which this method simply delegates to.
* 此方法为本地关闭上下文的{@link #close()} 的代理。
* @see #close()
*/
@Override
public void destroy() {
close();
}
/**
* Close this application context, destroying all beans in its bean factory.
* 关闭应用上下文,销毁所有bean工厂中的bean。
* <p>Delegates to {@code doClose()} for the actual closing procedure.
* Also removes a JVM shutdown hook, if registered, as it's not needed anymore.
* 代理{@code doClose()}方法,完成实际的关闭过程。
* 同时移除虚拟机关闭Hook,如果注册移除不需要的hook。
* @see #doClose()
* @see #registerShutdownHook()
*/
@Override
public void close() {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
doClose();
// If we registered a JVM shutdown hook, we don't need it anymore now:
// We've already explicitly closed the context.
if (this.shutdownHook != null) {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// ignore - VM is already shutting down
}
}
}
}
从上来看,销毁应用上下文,和关闭应用上下文实际委托给doClose操作,完成的任务和虚拟机关闭Hook线程相同,不同的是,在关闭应用上下文的时候, 如果关闭Hook不为空,要从运行时环境中移除关闭Hook线程。
BeanFactory接口实现
这里我们只简单的看几个操作,实际是委托给内部的bean工厂,更多见附。
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBean(name);
}
@Override
public <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBean(name, requiredType);
}
@Override
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBean(requiredType);
}
MessageSource接口实现
/**
* 消息源接口MessageSource的实现。
* 主要操作为获取本地化的消息,具体委托给上下文内部的消息源。
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of MessageSource interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public String getMessage(String code, Object args[], String defaultMessage, Locale locale) {
return getMessageSource().getMessage(code, args, defaultMessage, locale);
}
@Override
public String getMessage(String code, Object args[], Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException {
return getMessageSource().getMessage(code, args, locale);
}
@Override
public String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException {
return getMessageSource().getMessage(resolvable, locale);
}
/**
* Return the internal MessageSource used by the context.
* 返回上下文内部使用的消息源。
* @return the internal MessageSource (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalStateException if the context has not been initialized yet
*/
private MessageSource getMessageSource() throws IllegalStateException {
if (this.messageSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("MessageSource not initialized - " +
"call 'refresh' before accessing messages via the context: " + this);
}
return this.messageSource;
}
/**
* Return the internal message source of the parent context if it is an
* AbstractApplicationContext too; else, return the parent context itself.
* 如果消息为抽象应用上下文,则返回父类的内部消息源,否则返回类上下文
*/
protected MessageSource getInternalParentMessageSource() {
return (getParent() instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) ?
((AbstractApplicationContext) getParent()).messageSource : getParent();
}
从上面可以看出消息源接口的实现委托给内部的消息源。
获取给定位置的资源
/**
* 资源匹配模式解决器接口ResourcePatternResolver的实现。
* 主要操作为获取给定位置模式的资源。具体委托给上下文内部的资源模式解决器PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of ResourcePatternResolver interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
return this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(locationPattern);
}
从上面可以看出,获取给定位置的资源实际委托给内部的资源模式解决器。
Lifecycle生命周期接口实现
/**
* 生命周期接口的实现。
* 主要有启动和关闭操作,具体实现为调用上下文生命周期处理器的相应方法,并发布相关事件。
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of Lifecycle interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public void start() {
getLifecycleProcessor().start();
publishEvent(new ContextStartedEvent(this));
}
@Override
public void stop() {
getLifecycleProcessor().stop();
publishEvent(new ContextStoppedEvent(this));
}
@Override
public boolean isRunning() {
return (this.lifecycleProcessor != null && this.lifecycleProcessor.isRunning());
}
Lifecycle生命周期接口的启动和停止实际是调用应用上下文的生命周期处理器的启动和停止操作。应用上下文的默认生命周期处理器为,DefaultLifecycleProcessor, 具体启动和停止所做的任务可以查看DefaultLifecycleProcessor源码,我们前面文章中也有讲述。
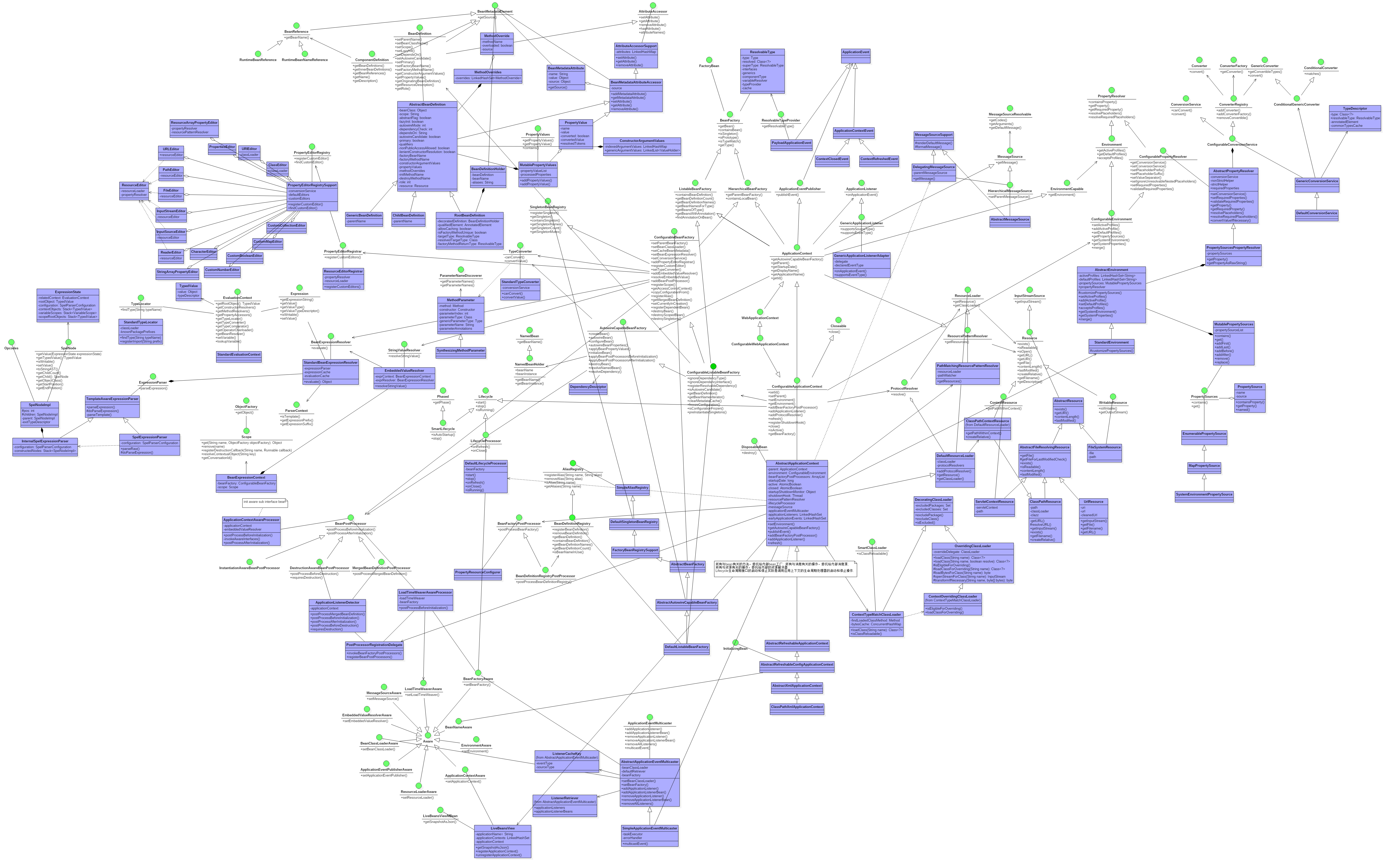
最后我们以AbstractApplicationContext的类图结束这篇文章。

总结
注册虚拟机关闭Hook,委托给运行时Runtime,而hook线程完成实际工作为,从LiveBeansView反注册当前应用上下文, 发布上下文关闭事件ContextClosedEvent,销毁上下文bean工厂中所有缓存的单例bean,关闭上下文状态closeBeanFactory,如果希望, 可以让子类做一些其他清除工作onClose;closeBeanFactory和onClose方法待子类扩展。
销毁应用上下文,和关闭应用上下文实际委托给doClose操作,完成的任务和虚拟机关闭Hook线程相同,不同的是,在关闭应用上下文的时候, 如果关闭Hook不为空,要从运行时环境中移除关闭Hook线程。
bean工厂接口,可配置、层级bean工厂接口的操作实现实际委托给内部bean工厂。MessageSource接口实现委托给内部的消息源。获取给定位置的资源实际委托给内部的资源模式解决器。
Lifecycle生命周期接口的启动和停止实际是调用应用上下文的生命周期处理器的启动和停止操作。
附
BeanFactory接口全部实现
/**
* 下面是bean工厂接口BeanFactory的实现方法,首先断言bean工厂处于激活状态,然后再将实际的操作,委托给内部bean工厂。
* 主要方法根据name或类型,或两者都有的对应的bean实例;判断bean是否存在,以及判断bean是否为单例或者原型模式bean操作。
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of BeanFactory interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBean(name);
}
@Override
public <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBean(name, requiredType);
}
@Override
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBean(requiredType);
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBean(name, args);
}
@Override
public <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBean(requiredType, args);
}
@Override
public boolean containsBean(String name) {
return getBeanFactory().containsBean(name);
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().isSingleton(name);
}
@Override
public boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().isPrototype(name);
}
@Override
public boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().isTypeMatch(name, typeToMatch);
}
@Override
public boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().isTypeMatch(name, typeToMatch);
}
@Override
public Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getType(name);
}
@Override
public String[] getAliases(String name) {
return getBeanFactory().getAliases(name);
}
/**
* 下面是List bean工厂接口ListableBeanFactory的具体实现,将实际操作委托给内部的bean工厂。
* 主要操作为判断给定name对应的bean定义是否存在,获取bean定义数量,获取所有bean定义的name集,
* 获取给定类型对应的bean name集或name与bean映射集,及获取待给定注解的bean name集或name与bean映射集
* 和获取给定name bean的注解。
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of ListableBeanFactory interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName) {
return getBeanFactory().containsBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
@Override
public int getBeanDefinitionCount() {
return getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinitionCount();
}
@Override
public String[] getBeanDefinitionNames() {
return getBeanFactory().getBeanDefinitionNames();
}
@Override
public String[] getBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type) {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(type);
}
@Override
public String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type) {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(type);
}
@Override
public String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit) {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
}
@Override
public <T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type) throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBeansOfType(type);
}
@Override
public <T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit)
throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBeansOfType(type, includeNonSingletons, allowEagerInit);
}
@Override
public String[] getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForAnnotation(annotationType);
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType)
throws BeansException {
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().getBeansWithAnnotation(annotationType);
}
@Override
public <A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class<A> annotationType)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException{
assertBeanFactoryActive();
return getBeanFactory().findAnnotationOnBean(beanName, annotationType);
}
/**
* 可继承bean工厂接口HierarchicalBeanFactory的实现。
* 主要操作获取父工厂,判断是否包含给定name对应的bean。
*/
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Implementation of HierarchicalBeanFactory interface
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public BeanFactory getParentBeanFactory() {
return getParent();
}
@Override
public boolean containsLocalBean(String name) {
return getBeanFactory().containsLocalBean(name);
}
/**
* Return the internal bean factory of the parent context if it implements
* ConfigurableApplicationContext; else, return the parent context itself.
* 如果上下文实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext,返回上下文的内部bean工厂,否则返回父类上下文。
* @see org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#getBeanFactory
*/
protected BeanFactory getInternalParentBeanFactory() {
return (getParent() instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) ?
((ConfigurableApplicationContext) getParent()).getBeanFactory() : getParent();
}