BeanDefinition接口定义
write by donaldhan, 2017-12-26 11:12引言
先来回顾一下,上一篇文章MutablePropertySources定义,MutablePropertySources为属性源Holder PropertySource的具体实现,内部通过一个属性源集合(CopyOnWriteArrayList)来管理内部的属性源,主要提供添加、移除、替换、是否包含属性源操作,这些操作实际上通过 CopyOnWriteArrayList 的相应操作完成。
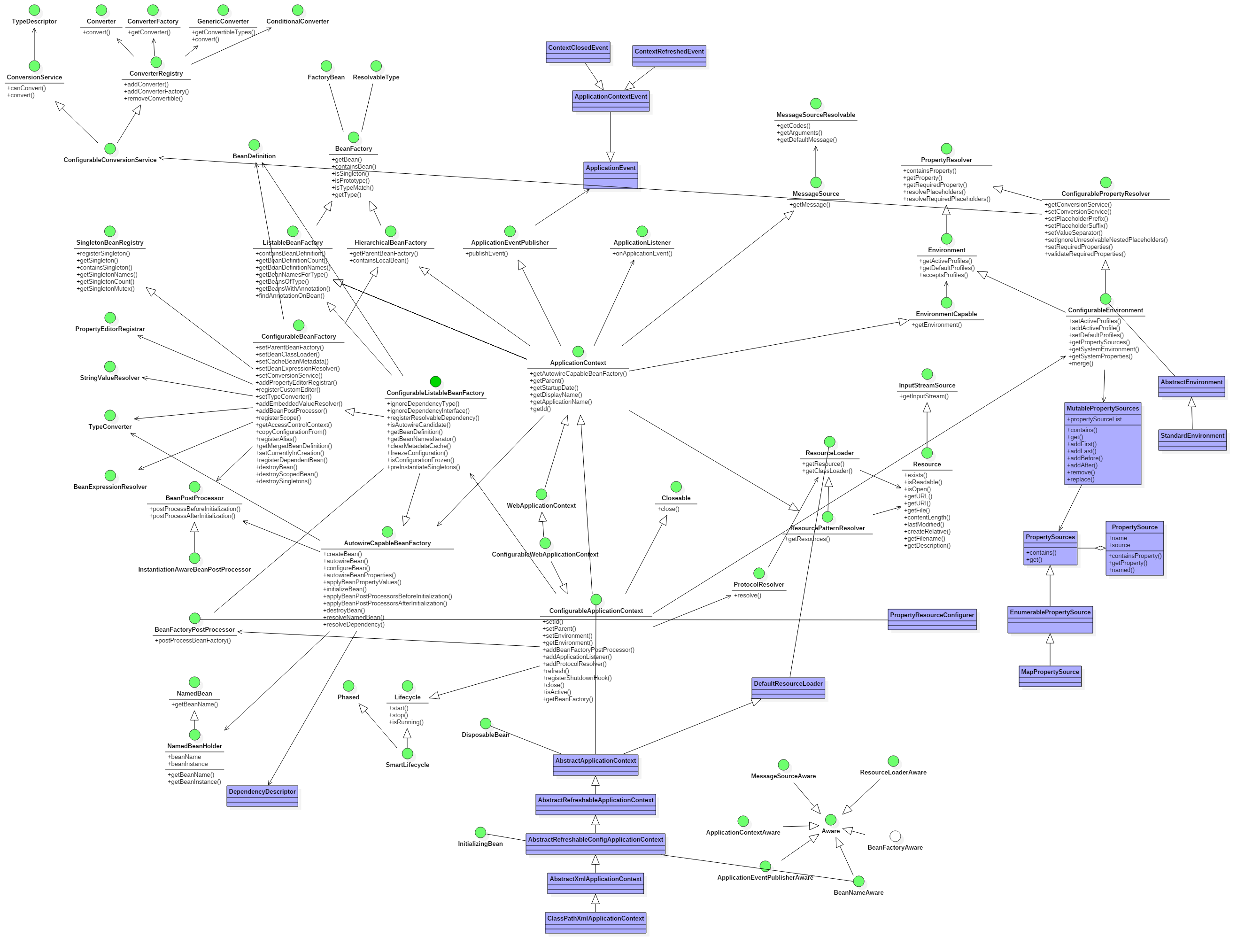
在ConfigurableListableBeanFactory接口定义中,提供了一个操作为获取给定name的bean的定义 BeanDefinition。由于篇幅问题,我们没有将 BeanDefinition, 今天我们就来BeanDefinition的接口定义。
目录
BeanDefinition接口定义
源码参见:BeanDefinition
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanMetadataElement;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.core.AttributeAccessor;
/**
* A BeanDefinition describes a bean instance, which has property values,
* constructor argument values, and further information supplied by
* concrete implementations.
*bean定义BeanDefinition描述一个bean实例,即属性值和构造参数,具体的实现提供的更多信息。
* <p>This is just a minimal interface: The main intention is to allow a
* {@link BeanFactoryPostProcessor} such as {@link PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer}
* to introspect and modify property values and other bean metadata.
*这个仅仅是一个最小化的接口,主要的作用是允许bean工厂后处理器,可以内省和修改属性值及其他bean元数据。
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Rob Harrop
* @since 19.03.2004
* @see ConfigurableListableBeanFactory#getBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ChildBeanDefinition
*/
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
/**
* Scope identifier for the standard singleton scope: "singleton".
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* 标准单例作用域,拓展bean工厂也许支持更多的作用域。
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
/**
* Scope identifier for the standard prototype scope: "prototype".
* <p>Note that extended bean factories might support further scopes.
* 标准原型作用域,拓展bean工厂也许支持更多的作用域。
* @see #setScope
*/
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a major part
* of the application. Typically corresponds to a user-defined bean.
* 表示一个应用的主要组成部分,比如一个用户定义的bean。
*/
int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is a supporting
* part of some larger configuration, typically an outer
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* 表示一个支持一些比较大的配置的bean定义,如一个外部的组件定义,{@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}
* {@code SUPPORT} beans are considered important enough to be aware
* of when looking more closely at a particular
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition},
* but not when looking at the overall configuration of an application.
*
*/
int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1;
/**
* Role hint indicating that a {@code BeanDefinition} is providing an
* entirely background role and has no relevance to the end-user. This hint is
* used when registering beans that are completely part of the internal workings
* of a {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing.ComponentDefinition}.
* 表示一个内部使用的注册的bean组件定义,与终端用户无关。
*/
int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2;
// Modifiable attributes
/**
* Set the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
* 设置bean定义的父name
*/
void setParentName(String parentName);
/**
* Return the name of the parent definition of this bean definition, if any.
* 获取bean定义的父name
*/
String getParentName();
/**
* Specify the bean class name of this bean definition.
* <p>The class name can be modified during bean factory post-processing,
* typically replacing the original class name with a parsed variant of it.
* 设置bean定义的bean class name。在bean工厂后处理的过程中,类名可以被修改,典型的情况下,
* 将原始class的name,替换成一个可解析的变量。
* @see #setParentName
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setBeanClassName(String beanClassName);
/**
* Return the current bean class name of this bean definition.
* 获取当前bean定义的name。
* <p>Note that this does not have to be the actual class name used at runtime, in
* case of a child definition overriding/inheriting the class name from its parent.
* Also, this may just be the class that a factory method is called on, or it may
* even be empty in case of a factory bean reference that a method is called on.
* Hence, do <i>not</i> consider this to be the definitive bean type at runtime but
* rather only use it for parsing purposes at the individual bean definition level.
* 需要注意的时,在孩子定义重写或从父类继承的name的情况下,此方法可能返回的不是实际运行环境下的class的name。
* 在工厂bean引用方法调用的情况下,此方法仅仅返回工厂方法的调用者,也许为空。因此,此方法不能用于运行时环境下,获取bean的类型
* ,仅仅用于在bean定义的层面上解析的目的。
* @see #getParentName()
* @see #getFactoryBeanName()
* @see #getFactoryMethodName()
*/
String getBeanClassName();
/**
* Override the target scope of this bean, specifying a new scope name.
* 重写bean定义的作用域。
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
void setScope(String scope);
/**
* Return the name of the current target scope for this bean,
* 获取bean的作用域
* or {@code null} if not known yet.
*/
String getScope();
/**
* Set whether this bean should be lazily initialized.
* <p>If {@code false}, the bean will get instantiated on startup by bean
* factories that perform eager initialization of singletons.
* 设置是否懒加载,如果为false,在bean工厂启动的时候,将会执行单例bean的预初始化。
*/
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);
/**
* Return whether this bean should be lazily initialized, i.e. not
* eagerly instantiated on startup. Only applicable to a singleton bean.
* 返回bean是否为懒加载模式,不能用于在启动过程中的懒加载初始化,仅仅可以用于单例bean。
*/
boolean isLazyInit();
/**
* Set the names of the beans that this bean depends on being initialized.
* The bean factory will guarantee that these beans get initialized first.
* 设置bean初始化时依赖的bean的name。bean工厂在初始化bean的时候 ,保证先初始化依赖的bean。
*/
void setDependsOn(String... dependsOn);
/**
* Return the bean names that this bean depends on.
* 返回bean依赖的bean的name集。
*/
String[] getDependsOn();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
* 设置bean是否可以作为其他bean的自动注入对象。
* <p>Note that this flag is designed to only affect type-based autowiring.
* It does not affect explicit references by name, which will get resolved even
* if the specified bean is not marked as an autowire candidate. As a consequence,
* autowiring by name will nevertheless inject a bean if the name matches.
* 需要注意的是,此标志仅仅用于基于类型的自动注入。此方法不会显示地影响以name方法的bean的引用,以name方法引用的bean,
* 将会使用没有被标注为可自动注入的bean。因此依赖于name的自动注入,坚决不会注意name匹配的bean。
*/
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a candidate for getting autowired into some other bean.
* 判断bean是否可以作为其他bean的自动注入对象
*/
boolean isAutowireCandidate();
/**
* Set whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
* <p>If this value is {@code true} for exactly one bean among multiple
* matching candidates, it will serve as a tie-breaker.
* 设置bean是否为主要的自动注入候选者。如果多个类型匹配返回true,则以primary bean注入。
*/
void setPrimary(boolean primary);
/**
* Return whether this bean is a primary autowire candidate.
* 判断bean是否为主要的自动注入候选者。
*/
boolean isPrimary();
/**
* Specify the factory bean to use, if any.
* This the name of the bean to call the specified factory method on.
* 设置工厂bean的name,bean的name可以被工厂方法使用。
* @see #setFactoryMethodName
*/
void setFactoryBeanName(String factoryBeanName);
/**
* Return the factory bean name, if any.
* 返回工厂bean的name
*/
String getFactoryBeanName();
/**
* Specify a factory method, if any. This method will be invoked with
* constructor arguments, or with no arguments if none are specified.
* The method will be invoked on the specified factory bean, if any,
* or otherwise as a static method on the local bean class.
* 设置工厂bean方法。此方法调用将会使用构造参数,如果没有方法,则没有参数。
* 此方法将会被特定的工厂bean调用,或者本地bean类型的静态方法调用。
*
* @see #setFactoryBeanName
* @see #setBeanClassName
*/
void setFactoryMethodName(String factoryMethodName);
/**
* Return a factory method, if any.
* 获取工厂方法
*/
String getFactoryMethodName();
/**
* Return the constructor argument values for this bean.
* 返回bean的构造参数值。
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* 在bean工厂后处理的过程中,返回的实例可以本修改。
* @return the ConstructorArgumentValues object (never {@code null})
*/
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();
/**
* Return the property values to be applied to a new instance of the bean.
* <p>The returned instance can be modified during bean factory post-processing.
* 返回将要应用到bean新实例的属性值。在bean工厂后处理的过程中,返回的实例可以本修改。
* @return the MutablePropertyValues object (never {@code null})
*/
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();
// Read-only attributes
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Singleton</b>, with a single, shared instance
* returned on all calls.
* 判断bean是否为单例共享实例。
* @see #SCOPE_SINGLETON
*/
boolean isSingleton();
/**
* Return whether this a <b>Prototype</b>, with an independent instance
* returned for each call.
* 判断bean是否为原型bean实例。
* @since 3.0
* @see #SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
*/
boolean isPrototype();
/**
* Return whether this bean is "abstract", that is, not meant to be instantiated.
* 判断bean是否为抽象类,意味着不可实例化
*/
boolean isAbstract();
/**
* Get the role hint for this {@code BeanDefinition}. The role hint
* provides the frameworks as well as tools with an indication of
* the role and importance of a particular {@code BeanDefinition}.
* 获取bean定义的角色。
* @see #ROLE_APPLICATION
* @see #ROLE_SUPPORT
* @see #ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
*/
int getRole();
/**
* Return a human-readable description of this bean definition.
* 返回bean定义的描述
*/
String getDescription();
/**
* Return a description of the resource that this bean definition
* came from (for the purpose of showing context in case of errors).
* 返回bean定义资源的描述
*/
String getResourceDescription();
/**
* Return the originating BeanDefinition, or {@code null} if none.
* 返回原始的bean定义,如果没有,则为null。
* Allows for retrieving the decorated bean definition, if any.
* <p>Note that this method returns the immediate originator. Iterate through the
* originator chain to find the original BeanDefinition as defined by the user.
* 此方法将返回即时的originator,通过迭代originator链,可以获取用户定义的原始bean定义。
*/
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
}
从上面可以看出,BeanDefinition接口用于描述一个bean实例的属性及构造参数等元数据;主要提供了父beanname,bean类型名,作用域,懒加载, bean依赖,自动注入候选bean,自动注入候选主要bean熟悉的设置与获取操作。同时提供了判断bean是否为单例、原型模式、抽象bean的操作,及获取bean的描述,资源描述,属性源,构造参数,原始bean定义等操作。
AttributeAccessor
源码参见:AttributeAccessor
package org.springframework.core;
/**
* Interface defining a generic contract for attaching and accessing metadata
* to/from arbitrary objects.
*AttributeAccessor接口定义了设置和访问对象属性的一般方式。
* @author Rob Harrop
* @since 2.0
*/
public interface AttributeAccessor {
/**
* Set the attribute defined by {@code name} to the supplied {@code value}.
* If {@code value} is {@code null}, the attribute is {@link #removeAttribute removed}.
* 设置name的属性值为value。如果值为null,则属性将被#removeAttribute方法移除。
* <p>In general, users should take care to prevent overlaps with other
* metadata attributes by using fully-qualified names, perhaps using
* class or package names as prefix.
* 在一般情况下,用户应该考虑使用全限定name,以避免被覆盖,可以考虑使用类型或包名做前缀。
* @param name the unique attribute key
* @param value the attribute value to be attached
*/
void setAttribute(String name, Object value);
/**
* Get the value of the attribute identified by {@code name}.
* Return {@code null} if the attribute doesn't exist.
* 获取属性name对应的值,没有则为null。
* @param name the unique attribute key
* @return the current value of the attribute, if any
*/
Object getAttribute(String name);
/**
* Remove the attribute identified by {@code name} and return its value.
* Return {@code null} if no attribute under {@code name} is found.
* 移除name对应的属性,并返回对应值。如果没有对应的属性,将会返回null。
* @param name the unique attribute key
* @return the last value of the attribute, if any
*/
Object removeAttribute(String name);
/**
* Return {@code true} if the attribute identified by {@code name} exists.
* Otherwise return {@code false}.
* 判断是否存在对应的name属性。
* @param name the unique attribute key
*/
boolean hasAttribute(String name);
/**
* Return the names of all attributes.
* 返回所有的属性
*/
String[] attributeNames();
}
从上面可以看出,AttributeAccessor接口主要提供了,设置获取属性值,移除属性,判断是否包含给定的属性等操作。
BeanMetadataElement
源码参见:BeanMetadataElement
package org.springframework.beans;
/**
* Interface to be implemented by bean metadata elements
* that carry a configuration source object.
* BeanMetadataElement接口的实现可以是一个携带配置源的bean元数据元素。
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0
*/
public interface BeanMetadataElement {
/**
* Return the configuration source {@code Object} for this metadata element
* (may be {@code null}).
* 返回当前bean元数据的配置数据源,没有则返回null
*/
Object getSource();
}
从上可以看出,BeanMetadataElement接口主要提供了获取bean元数据元素配置源的操作。
BeanDefinition的角色种类有3中一种用户定义的bean,一种适用于配置的组件bean,还有一种bean工厂内部的bean。配置组件bean的定义为ComponentDefinition,我们再来看一组件定义。
ComponentDefinition
源码参见:ComponentDefinition
package org.springframework.beans.factory.parsing;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanMetadataElement;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanReference;
/**
* Interface that describes the logical view of a set of {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions}
* and {@link BeanReference BeanReferences} as presented in some configuration context.
* 组件定义接口ComponentDefinition描述着配置上下文中的bean定义BeanDefinition和bean引用BeanReferences的一个逻辑视图。
* <p>With the introduction of {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandler pluggable custom XML tags},
* it is now possible for a single logical configuration entity, in this case an XML tag, to
* create multiple {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions} and {@link BeanReference RuntimeBeanReferences}
* in order to provide more succinct configuration and greater convenience to end users. As such, it can
* no longer be assumed that each configuration entity (e.g. XML tag) maps to one {@link BeanDefinition}.
* 为了提供更简约方便的配置,在xml配置 中当前可以通过一个单独的逻辑配置实体(XML标记),创建多个bean定义{@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions}和bean引用
* {@link BeanReference RuntimeBeanReferences}
* For tool vendors and other users who wish to present visualization or support for configuring Spring
* applications it is important that there is some mechanism in place to tie the {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions}
* in the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} back to the configuration data in a way
* that has concrete meaning to the end user. As such, {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandler}
* implementations are able to publish events in the form of a {@code ComponentDefinition} for each
* logical entity being configured. Third parties can then {@link ReaderEventListener subscribe to these events},
* allowing for a user-centric view of the bean metadata.
*
* <p>Each {@code ComponentDefinition} has a {@link #getSource source object} which is configuration-specific.
* In the case of XML-based configuration this is typically the {@link org.w3c.dom.Node} which contains the user
* supplied configuration information. In addition to this, each {@link BeanDefinition} enclosed in a
* {@code ComponentDefinition} has its own {@link BeanDefinition#getSource() source object} which may point
* to a different, more specific, set of configuration data. Beyond this, individual pieces of bean metadata such
* as the {@link org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue PropertyValues} may also have a source object giving an
* even greater level of detail. Source object extraction is handled through the
* {@link SourceExtractor} which can be customized as required.
*每个组件定义ComponentDefinition有一个配置源,可以通过{@link #getSource source object}获取。在基于xml的配置中,{@link org.w3c.dom.Node}
*包含用于提供的配置信息。每个bean定义包含于拥有bean定义源{@link BeanDefinition#getSource() source object}的组件定义中,源对象可能是
*一个不同的,精确的配置数据集。除此 之外,一些bean的元数据,比如属性值{@link org.springframework.beans.PropertyValue PropertyValues},
*也许有一个源对象,如果需要可以通过{@link SourceExtractor}去定制.
* <p>Whilst direct access to important {@link BeanReference BeanReferences} is provided through
* {@link #getBeanReferences}, tools may wish to inspect all {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions} to gather
* the full set of {@link BeanReference BeanReferences}. Implementations are required to provide
* all {@link BeanReference BeanReferences} that are required to validate the configuration of the
* overall logical entity as well as those required to provide full user visualisation of the configuration.
* It is expected that certain {@link BeanReference BeanReferences} will not be important to
* validation or to the user view of the configuration and as such these may be ommitted. A tool may wish to
* display any additional {@link BeanReference BeanReferences} sourced through the supplied
* {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions} but this is not considered to be a typical case.
*
* <p>Tools can determine the important of contained {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions} by checking the
* {@link BeanDefinition#getRole role identifier}. The role is essentially a hint to the tool as to how
* important the configuration provider believes a {@link BeanDefinition} is to the end user. It is expected
* that tools will <strong>not</strong> display all {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions} for a given
* {@code ComponentDefinition} choosing instead to filter based on the role. Tools may choose to make
* this filtering user configurable. Particular notice should be given to the
* {@link BeanDefinition#ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE INFRASTRUCTURE role identifier}. {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions}
* classified with this role are completely unimportant to the end user and are required only for
* internal implementation reasons.
*
* @author Rob Harrop
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0
* @see AbstractComponentDefinition
* @see CompositeComponentDefinition
* @see BeanComponentDefinition
* @see ReaderEventListener#componentRegistered(ComponentDefinition)
*/
public interface ComponentDefinition extends BeanMetadataElement {
/**
* Get the user-visible name of this {@code ComponentDefinition}.
* <p>This should link back directly to the corresponding configuration data
* for this component in a given context.
* 获取用户可见的组件定义ComponentDefinition的name,与组件在上下文中的配置数据相关联。
*/
String getName();
/**
* Return a friendly description of the described component.
* <p>Implementations are encouraged to return the same value from
* {@code toString()}.
* 返回组件的描述,具体的实现建议和{@code toString()}方法的返回值一样。
*/
String getDescription();
/**
* Return the {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions} that were registered
* to form this {@code ComponentDefinition}.
* 返回注册到组件的bean定义。
* <p>It should be noted that a {@code ComponentDefinition} may well be related with
* other {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions} via {@link BeanReference references},
* however these are <strong>not</strong> included as they may be not available immediately.
* Important {@link BeanReference BeanReferences} are available from {@link #getBeanReferences()}.
* 需要注意的是,组件定义{@code ComponentDefinition}可能通过bean引用BeanReference与其他bean定义关联,
* 然而这些不包括在内。但关联的bean引用可以通过 {@link #getBeanReferences()}获取。
* @return the array of BeanDefinitions, or an empty array if none
*/
BeanDefinition[] getBeanDefinitions();
/**
* Return the {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions} that represent all relevant
* inner beans within this component.
* 返回所有组件表示相关内部bean的定义。
* <p>Other inner beans may exist within the associated {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions},
* however these are not considered to be needed for validation or for user visualization.
* 其他bean定义内部的bean定义将不会被考虑在内。
* @return the array of BeanDefinitions, or an empty array if none
*/
BeanDefinition[] getInnerBeanDefinitions();
/**
* Return the set of {@link BeanReference BeanReferences} that are considered
* to be important to this {@code ComponentDefinition}.
* 组件定义需要考虑的bean的引用BeanReferences集。
* <p>Other {@link BeanReference BeanReferences} may exist within the associated
* {@link BeanDefinition BeanDefinitions}, however these are not considered
* to be needed for validation or for user visualization.
* {@link BeanReference BeanReferences}也许存在与一个关联的bean定义内,然而
* 在验证和用户可视化的过程中,这些将不会被考虑。
* @return the array of BeanReferences, or an empty array if none
*/
BeanReference[] getBeanReferences();
}
从上面可以出,组件定义ComponentDefinition接口主要提供了获取组件定义内部的bean定义,注册到组件的bean定义,及组件内部的bean引用。需要注意的是,组件定义{@code ComponentDefinition}可能通过bean引用BeanReference与其他bean定义关联,然而这些不包括在内注册bean定义的范畴,但关联的bean引用可以通过 {@link #getBeanReferences()}获取。同时获取bean定义的连个操作,都不包括bean定义内部的bean定义。
BeanReference
源码参见:BeanReference
import org.springframework.beans.BeanMetadataElement;
/**
* Interface that exposes a reference to a bean name in an abstract fashion.
* This interface does not necessarily imply a reference to an actual bean
* instance; it just expresses a logical reference to the name of a bean.
*BeanReference接口以一种抽象的方式,暴露了bean的name的引用。此接口不需要引用实际的bean的实例;
*仅仅表示一个bean的name的逻辑引用。
* <p>Serves as common interface implemented by any kind of bean reference
* holder, such as {@link RuntimeBeanReference RuntimeBeanReference} and
* {@link RuntimeBeanNameReference RuntimeBeanNameReference}.
* Spring提供了多种bean引用的实现,比如运行时bean应用RuntimeBeanReference和运行时bean name引用RuntimeBeanNameReference
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.0
*/
public interface BeanReference extends BeanMetadataElement {
/**
* Return the target bean name that this reference points to (never {@code null}).
* 返回应用bean的name
*/
String getBeanName();
}
从上可以看出,BeanReference接口提供了获取bean的name的操作。
最后我们以BeanDefinition的类图结束这篇文章。

总结
BeanDefinition接口用于描述一个bean实例的属性及构造参数等元数据;主要提供了父beanname,bean类型名,作用域,懒加载, bean依赖,自动注入候选bean,自动注入候选主要bean熟悉的设置与获取操作。同时提供了判断bean是否为单例、原型模式、抽象bean的操作,及获取bean的描述,资源描述,属性源,构造参数,原始bean定义等操作。
AttributeAccessor接口主要提供了,设置获取属性值,移除属性,判断是否包含给定的属性等操作。
BeanMetadataElement接口主要提供了获取bean元数据元素配置源的操作。
BeanReference接口提供了获取bean的name的操作。
组件定义ComponentDefinition接口主要提供了获取组件定义内部的bean定义,注册到组件的bean定义,及组件内部的bean引用。需要注意的是,组件定义{@code ComponentDefinition}可能通过bean引用BeanReference与其他bean定义关联,然而这些不包括在内注册bean定义的范畴,但关联的bean引用可以通过 {@link #getBeanReferences()}获取。同时获取bean定义的连个操作,都不包括bean定义内部的bean定义。