ApplicationContext接口定义
write by donaldhan, 2017-12-19 10:30引言
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext声明
上一篇文中我们,我们看了ClassPathXmlApplicationContext声明,并整理出ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的类图,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext直接或间接地实现了 EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourceLoader,Lifecycle,Closeable,BeanNameAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean 。今天我们先来看一应用上下文ApplicationContext接口及其父接口的定义。
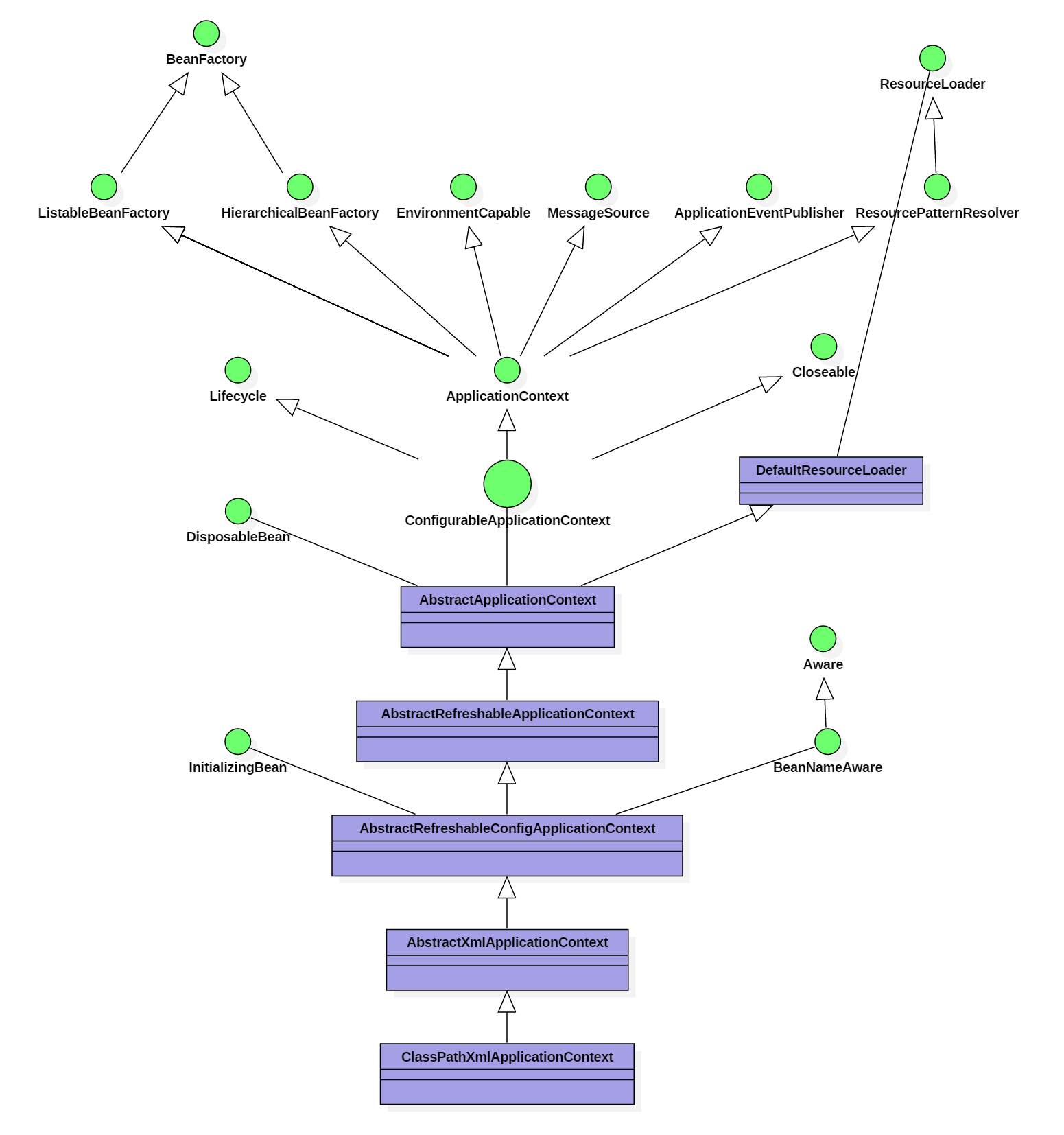
目录
父接口定义
我们先来看一下 BeanFactory 两个子类接口 ListableBeanFactory,HierarchicalBeanFactory 的定义,看之前,先看BeanFactory接口定义:
BeanFactory
BeanFactory接口源码参见BeanFactory
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
/**
* <p>Bean factory implementations should support the standard bean lifecycle interfaces
* as far as possible. The full set of initialization methods and their standard order is:
* 尽可能地bean工厂的实现,应该支持标准的bean生命周期接口,比如lifecycle。所有初始化方法和他们的标准顺序如下:
* <ol>
* <li>BeanNameAware's {@code setBeanName}
* <li>BeanClassLoaderAware's {@code setBeanClassLoader}
* <li>BeanFactoryAware's {@code setBeanFactory}
* <li>EnvironmentAware's {@code setEnvironment}
* <li>EmbeddedValueResolverAware's {@code setEmbeddedValueResolver}
* <li>ResourceLoaderAware's {@code setResourceLoader}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>ApplicationEventPublisherAware's {@code setApplicationEventPublisher}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>MessageSourceAware's {@code setMessageSource}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>ApplicationContextAware's {@code setApplicationContext}
* (only applicable when running in an application context)
* <li>ServletContextAware's {@code setServletContext}
* (only applicable when running in a web application context)
* <li>{@code postProcessBeforeInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors
* <li>InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* <li>a custom init-method definition
* <li>{@code postProcessAfterInitialization} methods of BeanPostProcessors
* </ol>
*
* <p>On shutdown of a bean factory, the following lifecycle methods apply:
* <ol>在关闭bean工厂之后,下面方法回调用
* <li>{@code postProcessBeforeDestruction} methods of DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors
* <li>DisposableBean's {@code destroy}
* <li>a custom destroy-method definition
* </ol>
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 13 April 2001
* @see BeanNameAware#setBeanName
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware#setBeanClassLoader
* @see BeanFactoryAware#setBeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher
* @see org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware#setMessageSource
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.web.context.ServletContextAware#setServletContext
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
* @see InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getInitMethodName
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization
* @see DisposableBean#destroy
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getDestroyMethodName
*/
public interface BeanFactory {
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
boolean containsBean(String name);
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
从上面可以看出,BeanFactory接口主要是主要提供了根据名称或类型获取bean的相关方法,以及判断bean是否匹配指定类型或判断 是否包含指定name的共享单实例或多实例bean。需要注意的是,如果bean工厂的实现是可继承工厂 HierarchicalBeanFactory,那么调用这些方法,如果没有在当前bean工厂实例中找到,将会从父工厂中查到。另外还需要注意一点,判断一个bean是否为共享单例模式,可以使用isSingleton方法,返回true,即是,返回false,并不能表示bean是多实例bean,具体要用isPrototype方法判断,同理isPrototype方法也是如此。
再来看ListableBeanFactory接口的定义:
ListableBeanFactory
具体ListableBeanFactory的源码,参见ListableBeanFactory
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
/**
*ListableBeanFactory扩展了bean工厂接口,ListableBeanFactory接口的实现可以列举所有bean实例,
*而不是作为一个请求客户端尝试以bean的名称,搜索bean。BeanFactory实现将会预先加载所有配置中BeanFactory
*的所有bean定义。
*如果bean工厂是一个可继承的bean工厂HierarchicalBeanFactory,返回值将不会考虑父类工厂bean,
*仅仅考虑与当前bean工厂关联的bean。BeanFactoryUtils工具类获取的祖先bean工厂,将考虑在内。
*接口方法,只会搜索当前bean工厂的bean定义。将会忽略所有通过ConfigurableBeanFactory的registerSingleton方法,
*注册到bean工厂的单例模式bean。
*注意:getBeanDefinitionCount和containsBeanDefinition方法异常情况,此方法不是设计为频繁调用的。
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 16 April 2001
* @see HierarchicalBeanFactory
* @see BeanFactoryUtils
*/
public interface ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
String[] getBeanNamesForType(ResolvableType type);
String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type);
String[] getBeanNamesForType(Class<?> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit);
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type) throws BeansException;
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(Class<T> type, boolean includeNonSingletons, boolean allowEagerInit)
throws BeansException;
String[] getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);
Map<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) throws BeansException;
<A extends Annotation> A findAnnotationOnBean(String beanName, Class<A> annotationType)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
}
从ListableBeanFactory的定义,可以看出ListableBeanFactory接口主要提供了判断是否存在给定name的bean定义,获取bean定义数量,获取指定类型的bean定义的name集或name与bean实例的映射集,获取待指定注解的bean定义的name或name与bean实例的映射集,以及获取给定name对应的bean的注定注解实例。需要注意的是,提供的操作不会到可继承bean工厂中去搜索,但包括BeanFactoryUtils工具类获取bean工厂的祖先bean工厂。另外getBeanNamesForType和getBeanNamesForAnnotation方法可以通过includeNonSingletons和allowEagerInit, 控制搜索bean的作用域范围和是否初始化懒加载单例模式bean与工厂bean。
再来看HierarchicalBeanFactory接口的定义:
HierarchicalBeanFactory
具体HierarchicalBeanFactory源码,参见[HierarchicalBeanFactory][] [HierarchicalBeanFactory]:https://github.com/Donaldhan/spring-framework/blob/4.3.x/spring-beans/src/main/java/org/springframework/beans/factory/HierarchicalBeanFactory.java “HierarchicalBeanFactory”
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
/**
*HierarchicalBeanFactory作为bean工厂的实现,标志着为一个可继承的bean工厂。
*在ConfigurableBeanFactory接口的setParentBeanFactory方法,中可以配置bean工厂的父类工厂。
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 07.07.2003
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory#setParentBeanFactory
*/
public interface HierarchicalBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
BeanFactory getParentBeanFactory();
boolean containsLocalBean(String name);
}
从HierarchicalBeanFactory的定义来看,HierarchicalBeanFactory接口标志一个以可继承bean工厂,我们可以通过 ConfigurableBeanFactory 接口的 setParentBeanFactory 方法配置bean工厂的父类工厂,主要提供获取父工厂操作,以及判断在本地bean工厂中是否存在指定name对应的bean的操作,但忽略祖先上下文中的bean定义。
ApplicationEventPublisher
ApplicationEventPublisher的源码,参见ApplicationEventPublisher
package org.springframework.context;
/**
*ApplicationEventPublisher接口,封装了事件发布功能,作为ApplicationContext的父接口,
*服务于应用上下文ApplicationContext。
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 1.1.1
* @see ApplicationContext
* @see ApplicationEventPublisherAware
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent
* @see org.springframework.context.event.EventPublicationInterceptor
*/
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event);
void publishEvent(Object event);
}
从上面可看出,事件发布接口ApplicationEventPublisher,主要作为ApplicationContext的父接口,封装了事件发布功能,提供了事件发布功能。当事件发布时,通知所有注册到当前应用关注ApplicationEvent事件event的监听器,如果发布的事件不是 ApplicationEvent, 则将会包装成 PayloadApplicationEvent。
ApplicationEvent
再来简单看一下应用事件ApplicationEvent
package org.springframework.context;
import java.util.EventObject;
/**
*所有的应用事件,将会继承此类。抽象不意味着,一般的应用事件不可以直接发布。
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
*/
public abstract class ApplicationEvent extends EventObject {
/** use serialVersionUID from Spring 1.2 for interoperability */
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7099057708183571937L;
/** System time when the event happened 事件发生的系统时间*/
private final long timestamp;
public ApplicationEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public final long getTimestamp() {
return this.timestamp;
}
}
从上面可以看出,ApplicationEvent用于表示应用发生的事件,事件包括事件发生的时间和事件发生源。
我们再来看一下ApplicationEvent的父类EventObject,EventObject属于jdk的范畴。
package java.util;
/**
* <p>
* The root class from which all event state objects shall be derived.
所有事件状态对象的原始类。
* <p>
* All Events are constructed with a reference to the object, the "source",
* that is logically deemed to be the object upon which the Event in question
* initially occurred upon.
所有事件构造有一个对象已用,此对象用于表示,事件发生源。
*
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public class EventObject implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5516075349620653480L;
/**
* The object on which the Event initially occurred.
事件发生源
*/
protected transient Object source;
/**
* Constructs a prototypical Event.
*
* @param source The object on which the Event initially occurred.
* @exception IllegalArgumentException if source is null.
*/
public EventObject(Object source) {
if (source == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("null source");
this.source = source;
}
public Object getSource() {
return source;
}
...
}
从上面来看EventObject,表示一个事件对象,同时记录事件发生源。
ApplicationListener
再来看一下应用监听器ApplicationListener
package org.springframework.context;
import java.util.EventListener;
/**
* Interface to be implemented by application event listeners.
* Based on the standard {@code java.util.EventListener} interface
* for the Observer design pattern.。
*所有应用事件监听器将实现ApplicationListener接口。此接口基于标准的观察者模式的接口java.util.EventListener。
* <p>As of Spring 3.0, an ApplicationListener can generically declare the event type
* that it is interested in. When registered with a Spring ApplicationContext, events
* will be filtered accordingly, with the listener getting invoked for matching event
* objects only.
* 从spring3.0以后,应用监听器需要声明关注的应用事件类型。当监听器注册到spring的应用上下文ApplicationContext时,
* 将会根据事件类型过滤监听器,匹配事件类型的监听器才会被通知。
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @param <E> the specific ApplicationEvent subclass to listen to
* @see org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster
*/
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
/**
* Handle an application event.
* 处理应用事件
* @param event the event to respond to
*/
void onApplicationEvent(E event);
}
从上面可以看出,监听器接口ApplicationListener,是基于标准JDK的观察者模式的接口java.util.EventListener, 从spring3.0以后,应用监听器需要声明关注的应用事件类型。当监听器注册到spring的应用上下文ApplicationContext时, 将会根据事件类型过滤监听器,匹配事件类型的监听器才会被通知。接口主要提供了处理事件操作。
来简单看一下jdk的事件监听器接口的声明:
package java.util;
/**
* A tagging interface that all event listener interfaces must extend.
* @since JDK1.1
*/
public interface EventListener {
}
从上面可以看出事件监听器接口,从JDK1.1,就已经出现。
我们接着看EnvironmentCapable接口
EnvironmentCapable
package org.springframework.core.env;
/**
* EnvironmentCapable表示一个组件包括一个或暴露一个Environment环境引用。
*Spring的所有应用上下文都是EnvironmentCapable接口实现,用于应用上下文与环境交互。
* 需要注意的是,ApplicationContext扩展了EnvironmentCapable接口,通过getEnvironment方法暴露环境配置;
* 然而ConfigurableApplicationContext将会重定义getEnvironment方法,返回一个ConfigurableEnvironment。
* 两种方法带来的效果是,在环境配置Environment对象在ConfigurableApplicationContext可访问以前,都是自读的,
* 可以理解为ConfigurableApplicationContext的getEnvironment方法返回的环境对象时可修改的。
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.1
* @see Environment
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment
* @see org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#getEnvironment()
*/
public interface EnvironmentCapable {
/**
* Return the {@link Environment} associated with this component
* (may be {@code null} or a default environment).
* 返回组件关联的环境Environment,没有则为空。
*/
Environment getEnvironment();
}
从上面可以看出,接口从spring3.1才使用,EnvironmentCapable接口,表示包括或暴露一个Environment环境引用的组件。Spring的所有应用上下文都是EnvironmentCapable接口实现,用于应用上下文与环境交互。需要注意的是,ApplicationContext扩展了EnvironmentCapable接口,通过getEnvironment方法暴露环境配置;然而 ConfigurableApplicationContext 将会重定义getEnvironment方法,返回一个ConfigurableEnvironment。 两种方法带来的效果是,在环境配置Environment对象在 ConfigurableApplicationContext 可访问以前,都是自读的,可以理解为 ConfigurableApplicationContext 的getEnvironment方法返回的环境象时可修改的。接口提供了获取环境配置操作。
我们再来看一下环境配置Environment接口的定义:
package org.springframework.core.env;
/**
*Environment接口表示当前应用正在运行的环境。应用环境的配置有两个方面:配置profiles与属性properties,属性相关的方法,
*通过Environment的父接口暴露属性访问方法。
*命名的配置profile,在配置激活的情况下,注册到容器的bean定义将会根据配置profile进行逻辑地分组。无论一个配置已通过xml或注解进行配置,
*没有bean都属于一个配置;具体参数spring-beans 3.1 的shema和@Profile注解的说明。可以通过getDefaultProfiles和getActiveProfiles方法
*来确定环境与配置的对象的关联关系。
* 属性配置在所有应用中,扮演者一个重要的角色,可以有不同种类的属性源:比如属性文件,java虚拟机系统属性,系统环境变量,JNDI,
* servlet上下文配置,ad-hoc属性对象,Map等。关联属性的环境对象,提供配置属性源和解决属性的一个方便的配置接口。
*
* 为了查询配置的状态或解决属性,应用上下文管理的bean,也许通过EnvironmentAware或依赖环境Environment的注解@Inject,注册到应用上下文。
*在大多说的情况下,应用层的bean不需要与环境直接进行交互,但需要使用属性placeholder配置器,配置替换形式如“${...}”
*的属性,比如PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer,本身即是一个EnvironmentAware,从spring3.1以后,
*当使用<context:property-placeholder/>配置属性配置器时,默认的配置将会配置激活。
* 环境配置对象必须通过ConfigurableEnvironment接口进行配置,所有AbstractApplicationContext的子类,都可通过getEnvironment方法
* 返回一个可配置环境接口ConfigurableEnvironment。
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.1
* @see PropertyResolver
* @see EnvironmentCapable
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment
* @see AbstractEnvironment
* @see StandardEnvironment
* @see org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware
* @see org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#getEnvironment
* @see org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#setEnvironment
* @see org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#createEnvironment
*/
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
/**
* 返回当前环境显示激活的配置集。配置用于创建有条件地注册bean定义的逻辑分组,比如基于开发环境的配置。配置可以通过设置系统属性
* {@linkplain AbstractEnvironment#ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
* "spring.profiles.active"}或者调用ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles(String...)方法配置。
* 如果没有配置显示激活, #getDefaultProfiles()返回的默认配置将会被自动激活。
* @see #getDefaultProfiles
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles
* @see AbstractEnvironment#ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
*/
String[] getActiveProfiles();
/**
* 当没有配置显示激活, 返回的默认将会被自动激活的配置集。
* @see #getActiveProfiles
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setDefaultProfiles
* @see AbstractEnvironment#DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME
*/
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
/**
* 判断一个或多个配置是否激活,或者在默认显示激活的配置情况下,一个或多个配置是否在默认的配置集。如果配置以'!'逻辑符开头,
* 表示当对应的配置没有开启时,返回true,比如env.acceptsProfiles("p1", "!p2"),如果'p1'激活,"!p2"没有激活,
* 将返回true。如果调用时0个参数,或者有一个配置为null,或空字符串等,将会抛出非法参数异常
* @see #getActiveProfiles
* @see #getDefaultProfiles
*/
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
}
从spring3.1开始,才出现Environment接口,Environment接口同时是一个 PropertyResolver 接口,提供了获取激活配置 Profiles 和默认配置的操作,同时提供了判断配置是否激活操作。应用环境Environment有一个或多个配置 Profiles,配置可以理解为配置集或类型,比如开发,测试,体验,生产等环境。当应用存在需要引用属性的情况,我们可以从环境中获取,应为环境是一个 PropertyResolver。环境配置对象必须通过ConfigurableEnvironment接口进行配置,所有AbstractApplicationContext的子类,都可通过getEnvironment方法返回一个可配置环境接口ConfigurableEnvironment。
PropertyResolver
我们简单看一下PropertyResolver接口
package org.springframework.core.env;
/**
* PropertyResolver是一个依赖于底层数据解决属性接口
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
* @see Environment
* @see PropertySourcesPropertyResolver
*/
public interface PropertyResolver {
/**
* 如果给定的key不为null,返回是否包含给定属性key
* i.e. if the value for the given key is not {@code null}.
*/
boolean containsProperty(String key);
/**
* 返回给定属性key的值,没有为null
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @see #getProperty(String, String)
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String)
*/
String getProperty(String key);
/**
* 返回给定属性key的值,没有返回默认值defaultValue
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String)
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
*/
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
/**
* 返回是给定类型属性key的值,没有为null
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param targetType the expected type of the property value
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* 返回是给定类型属性key的值,没有返回默认值defaultValue
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param targetType the expected type of the property value
* @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
/**
* 返回是给定类型属性key的值,如果值得类型不同,则进行转换,转换异常,则抛出ConversionException,没有对应的值,则返回null
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
* @deprecated as of 4.3, in favor of {@link #getProperty} with manual conversion
* to {@code Class} via the application's {@code ClassLoader}
*/
@Deprecated
<T> Class<T> getPropertyAsClass(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* 返回是给定属性key的值,没有抛出IllegalStateException
* @throws IllegalStateException if the key cannot be resolved
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 返回是给定类型属性key的值,没有抛出IllegalStateException
* @throws IllegalStateException if the given key cannot be resolved
*/
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 在给定上文本中,替换引用属性“${...}”,没有默认的情况下,则忽略,不做任何改变
* @param text the String to resolve
* @return the resolved String (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null}
* @see #resolveRequiredPlaceholders
* @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String)
*/
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
/**
* 此方法,与上面方法不同的是,没有匹配的值,则抛出异常IllegalArgumentException
* @return the resolved String (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null}
* or if any placeholders are unresolvable
* @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String, boolean)
*/
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
从上面可以看出从spring3.1开始,PropertyResolver才出现,PropertyResolver注意根据属性源,是否包含给定属性,获取相关属性的值及获取给定类型属性的值操作,同时提供了替换给定上文本中的引用属性“${…}”操作。
ResourcePatternResolver
具体源码参见:ResourcePatternResolver
package org.springframework.core.io.support;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
/**
* Strategy interface for resolving a location pattern (for example,
* an Ant-style path pattern) into Resource objects.
*ResourcePatternResolver接口将指定路径下的文件加载资源对象。
* <p>This is an extension to the {@link org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader}
* interface. A passed-in ResourceLoader (for example, an
* {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} passed in via
* {@link org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware} when running in a context)
* can be checked whether it implements this extended interface too.
*接口拓展了org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader接口。
* <p>{@link PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver} is a standalone implementation
* that is usable outside an ApplicationContext, also used by
* {@link ResourceArrayPropertyEditor} for populating Resource array bean properties.
*PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver接口是ResourcePatternResolver的一个独立是吸纳,不能在ApplicationContext外部使用,
*可以使用ResourceArrayPropertyEditor,设置bean的属性。
* <p>Can be used with any sort of location pattern (e.g. "/WEB-INF/*-context.xml"):
* Input patterns have to match the strategy implementation. This interface just
* specifies the conversion method rather than a specific pattern format.
*可以用于任何种类的位置模式(e.g. "/WEB-INF/*-context.xml"):输入的模式必须匹配指定的规则。
* <p>This interface also suggests a new resource prefix "classpath*:" for all
* matching resources from the class path. Note that the resource location is
* expected to be a path without placeholders in this case (e.g. "/beans.xml");
* JAR files or classes directories can contain multiple files of the same name.
*此接口建议以 "classpath*:"为前缀,创建一个匹配class路径的所有资源。需要注意的是,资源位置应该为一个路径,而不是没有占位符,
*比如 (e.g. "/beans.xml");jar包文件或多个相同名字的文件。
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 1.0.2
* @see org.springframework.core.io.Resource
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware
*/
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
/**
* Pseudo URL prefix for all matching resources from the class path: "classpath*:"
* This differs from ResourceLoader's classpath URL prefix in that it
* retrieves all matching resources for a given name (e.g. "/beans.xml"),
* for example in the root of all deployed JAR files.
* 所有匹配class路径的伪URL前缀“classpath*:”。以URL前缀“classpath*的开头的class路径资源,
* 与匹配给定name("/beans.xml")的ResourceLoader的以"classpath:"为前缀的资源不同,比如,JAR包的根目录。
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader#CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX
*/
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
/**
* Resolve the given location pattern into Resource objects.
* <p>Overlapping resource entries that point to the same physical
* resource should be avoided, as far as possible. The result should
* have set semantics.
* 将给定路径模式下的文件,转换成资源Resource对应。尽量避免在同级物理层环境,出现重叠的资源entries。
* 返回的结果为一个资源集。
* @param locationPattern the location pattern to resolve
* @return the corresponding Resource objects
* @throws IOException in case of I/O errors
*/
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
从上,可以看出,ResourcePatternResolver拓展了 ResourceLoader 接口,主要用于解决或加载给定路径下的资源文件,ResourcePatternResolver建议使用 以 “classpath*:”为前缀,创建一个匹配class路径的所有资源。
为了理解下面这个属性
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
,我们来看ResourceLoader
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
...
}
public abstract class ResourceUtils {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
public static final String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = "classpath:";
...
}
从上面可以看出,ResourcePatternResolver建议使用以 classpath: 为前缀,创建一个匹配class路径的所有资源,当然也可以是其他形式的位置模式。ResourceLoader的资源以 *classpath: 为前缀,这两种方式的不同,我们在看完ResourceLoader接口的定义,再来比较。
ResourceLoader
具体源码参见:ResourceLoader
package org.springframework.core.io;
import org.springframework.util.ResourceUtils;
/**
* Strategy interface for loading resources (e.. class path or file system
* resources). An {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext}
* is required to provide this functionality, plus extended
* {@link org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver} support.
*ResourceLoader是一个策略接口,用于加载资源(比如class路径或文件系统资源)。org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext
*需要提供这些功能,同时要拓展ResourcePatternResolver的支持。
* <p>{@link DefaultResourceLoader} is a standalone implementation that is
* usable outside an ApplicationContext, also used by {@link ResourceEditor}.
*默认资源加载器DefaultResourceLoader是一个独立的实现,可以在在应用上下文外部使用。也可以通过ResourceEditor使用。
* <p>Bean properties of type Resource and Resource array can be populated
* from Strings when running in an ApplicationContext, using the particular
* context's resource loading strategy.
* 当运行在应用上下文中,可以使用特殊的上下为资源加载策略,类型资源和资源数组可以从字符串构建bean的属性。
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 10.03.2004
* @see Resource
* @see org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware
*/
public interface ResourceLoader {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
/**
* 返回特殊位置资源的资源句柄。
* 资源句柄可以总是可以重用资源描述,允许多次调用Resource#getInputStream()方法获取资源输入流。
* 必须支持完全限定路径,如"file:C:/test.dat".
* <li>Must support classpath pseudo-URLs, e.g. "classpath:test.dat".
* 必须支持伪类路径URL,比如e.g. "classpath:test.dat".
* 应该支持相对路径的文件路径,比如"WEB-INF/test.dat".
* 这些需要具体的实现,典型的通过ApplicationContext提供实现
* 注意:一个资源handle不以为者,资源存在,可以调用Resource#exists检查资源是否存在。
* @param location the resource location
* @return a corresponding Resource handle (never {@code null})
* @see #CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX
* @see Resource#exists()
* @see Resource#getInputStream()
*/
Resource getResource(String location);
/**
* 暴露资源加载器ResourceLoader使用的类加载器。
* 客户端需要直接访问ClassLoader,可以使用ResourceLoader的统一管理器。
* @return the ClassLoader (only {@code null} if even the system
* ClassLoader isn't accessible)
* 如果系统类加载器不可访问,则返回null
* @see org.springframework.util.ClassUtils#getDefaultClassLoader()
*/
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
从上面可以看出,ResourceLoader接口用于加载资源class路径或文件系统等类型资源,提供获取给定位置的资源操作和获取系统ClassLoader。 再来简单看一下ClassUtils,获取类加载器
package org.springframework.util;
import java.beans.Introspector;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.IdentityHashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Miscellaneous class utility methods.
* Mainly for internal use within the framework.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Keith Donald
* @author Rob Harrop
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 1.1
* @see TypeUtils
* @see ReflectionUtils
*/
public abstract class ClassUtils {
public static ClassLoader getDefaultClassLoader() {
ClassLoader cl = null;
try {
//首先获取当前线程类加载器
cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Cannot access thread context ClassLoader - falling back...
}
if (cl == null) {
// No thread context class loader -> use class loader of this class.
//没有当前线程上下文,则使用当前类的类加载器
cl = ClassUtils.class.getClassLoader();
if (cl == null) {
// getClassLoader() returning null indicates the bootstrap ClassLoader
//否则返回系统的类加载器。
try {
cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Cannot access system ClassLoader - oh well, maybe the caller can live with null...
}
}
}
return cl;
}
}
从上可以看出,ResourceLoader获取类加载器,首先获取当前线程类加载器,如果没有当前线程上下文,则使用当前类的类加载器,如果当前类没有类加载器,则获取系统的类加载器。
Resource
具体源码参见:Resource
package org.springframework.core.io;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URL;
/**
*Resource接口表示一个资源描述符,即底层资源实例类型的抽象。比如文件,类路径资源。
*如果资源以物理形式存在,输入流可以被每个资源打开,但是一个URL或文件句柄,必须调整为确定的资源。
*实际的行为依赖于具体的实现。
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 28.12.2003
* @see #getInputStream()
* @see #getURL()
* @see #getURI()
* @see #getFile()
* @see WritableResource
* @see ContextResource
* @see UrlResource
* @see ClassPathResource
* @see FileSystemResource
* @see PathResource
* @see ByteArrayResource
* @see InputStreamResource
*/
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* 判断资源实际上是否以物理形式存在。
*/
boolean exists();
/**
* 判断资源的内容是否可以通过#getInputStream方法访问
* 对于特殊的资源描述,将会返回true,需要注意的是尝试读取实际的内容有可能会失败。
* 然而返回false,表示资源内容不可读。
* @see #getInputStream()
*/
boolean isReadable();
/**
* 判断一个资源是否是一个打开的流handle。如果返回true,输入流不能读取多次,
* 同时在读取后,要关闭资源,避免内存泄漏。对于特殊的资源描述,将会返回false。
*/
boolean isOpen();
/**
*返回资源的URL,如果资源不能够转化为URL,或资源不能够作为描述符访问,则抛出IO异常。
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* 返回资源的URI,如果资源不能够转化为URI,或资源不能够作为描述符访问,则抛出IO异常。
* @since 2.5
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* @see #getInputStream()
* 返回资源关联的文件句柄,如果文件不能够解决为一个绝对的文件路径,或在文件系统中,资源不可利用,
* 则抛出FileNotFoundException异常,对于一般的读或解决路径失败,则抛出IOException异常
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* Determine the content length for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved
* (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type)
* 获取资源内容的长度,如果资源在文件系统中或其他物理资源类型,不能够解决,则抛出IOException异常
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* Determine the last-modified timestamp for this resource.
* @throws IOException if the resource cannot be resolved
* (in the file system or as some other known physical resource type)
* 返回资源上次修改的时间戳,如果资源在文件系统中或其他物理资源类型,不能够解决,则抛出IOException异常
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* Create a resource relative to this resource.
* 创建资源的相对路径资源。
* @param relativePath the relative path (relative to this resource)
* @return the resource handle for the relative resource
* @throws IOException if the relative resource cannot be determined
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* Determine a filename for this resource, i.e. typically the last
* part of the path: for example, "myfile.txt".
* <p>Returns {@code null} if this type of resource does not
* have a filename.
* 获取资源的文件名
*/
String getFilename();
/**
* Return a description for this resource,
* to be used for error output when working with the resource.
* <p>Implementations are also encouraged to return this value
* from their {@code toString} method.
* 返回资源的描述符
* @see Object#toString()
*/
String getDescription();
}
从上面可以看出,Resource实际为一个输入流资源 InputStreamSource 接口,主要提供了获取资源URL,URI,对应的文件,文件名,上次修改时间戳,文件描述符操作,以及判断资源是否存在,是否可读,是否打开等操作。需要注意的是在读取资源后,要关闭资源,以防内存泄漏。
再来看一些Resource的父接口InputStreamSource。
InputStreamSource
具体源码参见:InputStreamSource
package org.springframework.core.io;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
*InputStreamSource是一个JDK的InputStream的源对象接口。
*此接口是资源拓展接口的基础接口。
* 对于一种用途的流,InputStreamResource可以用于任何给定的输入流InputStream。Spring的
* ByteArrayResource或其他基于文件的资源的实现都是一个具体的实例,允许多次读取底层流内容。
* 这个接口对于抽象流内容非常有用,比如mail的附加物。
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 20.01.2004
* @see java.io.InputStream
* @see Resource
* @see InputStreamResource
* @see ByteArrayResource
*/
public interface InputStreamSource {
/**
* 返回底层资源内容的输入流。期望每次调用创建一个fresh流。当考虑到API,比如JavaMail的时候,
* 输入流特别的重要,当创建mail的attachments时,需要多次读取流。在这种情况下,需要每次
* 调用返回一个fresh流。
* @return the input stream for the underlying resource (must not be {@code null})
* @throws java.io.FileNotFoundException if the underlying resource doesn't exist
* @throws IOException if the content stream could not be opened
*/
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}
从上可以看出,InputStreamSource主要提供了获取底层物理资源对应的输入流操作。
再来看MessageSource接口
MessageSource
具体源码参见:MessageSource
package org.springframework.context;
import java.util.Locale;
/**
*MessageSource接口用于解决消息,支持参数化和国际化消息。
*spring提供了两种开箱即用的实现,基于标准java.util.ResourceBundle的实现ResourceBundleMessageSource
*和在虚拟机没有重启的情况下可以重新加载消息定义的ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource。
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @see org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource
* @see org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource
*/
public interface MessageSource {
/**
* 尝试解决消息,如果没有消息发现,则返回默认的消息
* @param code
* 需要寻找的消息代码,比如'calculator.noRateSet'。使用此类,鼓励使用相关类型全限定的类型名
* 作为base的name,这样可以避免冲突,确保最大的清晰。
* @param args
* 参数值,用于填充消息中的占位符,比如 "{0}", "{1,date}", "{2,time}",没有则为null。
* @param defaultMessage
* 如果寻找失败,则返回默认的消息
* @param locale the locale in which to do the lookup
* 本地化参数
* @return the resolved message if the lookup was successful;
* otherwise the default message passed as a parameter
* @see java.text.MessageFormat
*/
String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, String defaultMessage, Locale locale);
/**
* 与上面方法不同的是,当消息不存在时,抛出NoSuchMessageException异常
* @see java.text.MessageFormat
*/
String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException;
/**
* 尝试解决MessageSourceResolvable中消息及消息中的参数。
* @throws NoSuchMessageException if the message wasn't found
* @see java.text.MessageFormat
*/
String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException;
}
从上面可以看出,MessageSource接口提供了获取指定 Locale 的消息操作,消息支持占位符和国际化。同时提供了解决 MessageSourceResolvable 中的消息。
再来看MessageSourceResolvable接口的定义。
MessageSourceResolvable
具体源码参见:MessageSourceResolvable
package org.springframework.context;
/**
*MessageSourceResolvable接口在MessageSource接口中用于消息解决。
*Spring的字节错误验证validation类实现了此接口
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @see MessageSource#getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable, java.util.Locale)
* @see org.springframework.validation.ObjectError
* @see org.springframework.validation.FieldError
*/
public interface MessageSourceResolvable {
/**
* 返回消息关联的code
* @return a String array of codes which are associated with this message
*/
String[] getCodes();
/**
* 返回消息中所有的参数
* @return an array of objects to be used as parameters to replace
* placeholders within the message text
* @see java.text.MessageFormat
*/
Object[] getArguments();
/**
* 返回默认的消息,如果没有则为null
* @return the default message, or {@code null} if no default
*/
String getDefaultMessage();
}
从上面可以看出,MessageSourceResolvable主要用于MessageSource接口的消息解决,提供了获取消息code,参数及默认消息操作。
ApplicationContext接口定义
具体源码参见:ApplicationContext
package org.springframework.context;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.HierarchicalBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.env.EnvironmentCapable;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver;
/**
* Central interface to provide configuration for an application.
* This is read-only while the application is running, but may be
* reloaded if the implementation supports this.
*应用上下文ApplicationContext接口是应用的配置中心接口。当应用已经运行时,应用上下文是只读的,
*但是,如果具体的应用上下文实现支持的话,也许可以重新加载。
* <p>An ApplicationContext provides:
* <ul>应用上下文提供如下:
* <li>Bean factory methods for accessing application components.
* Inherited from {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory}.
* bean工厂方法访问应用的组件,从org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory继承
* <li>The ability to load file resources in a generic fashion.
* Inherited from the {@link org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader} interface.
* 加载一般文件资源的能力,从org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader继承
* <li>The ability to publish events to registered listeners.
* Inherited from the {@link ApplicationEventPublisher} interface.
* 发布时间到监听器的功能,从 ApplicationEventPublisher继承。
* <li>The ability to resolve messages, supporting internationalization.
* Inherited from the {@link MessageSource} interface.
* 解决消息,支持国际化的功能,从MessageSource继承。
* <li>Inheritance from a parent context. Definitions in a descendant context
* will always take priority. This means, for example, that a single parent
* context can be used by an entire web application, while each servlet has
* its own child context that is independent of that of any other servlet.
* 父上下文的继承性(HierarchicalBeanFactory)。定义在子孙上下文中的bean定义将会有限考虑。这意味着,一个单独的父上下文可以被整个web应用上下文所使用,
* 然而每个servlet有自己额上下文,独立于其他servlet。这一点体现在,当我们使用spring的核心容器特性和spring mvc时,在web.xml中,
* 我们有两个配置一个是上下文监听器(org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener),
* 同时需要配置应用上下文bean的定义配置,一般是ApplicationContext.xml,另一个是Servlet分发器(org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet),
* 同时需要配置WebMVC相关配置,一般是springmvc.xml。应用一般运行的在Web容器中,Web容器可以访问应用上下文,同时Web容器的Servlet也可以访问应用上下文。
* </ul>
*
* <p>In addition to standard {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory}
* lifecycle capabilities, ApplicationContext implementations detect and invoke
* {@link ApplicationContextAware} beans as well as {@link ResourceLoaderAware},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware} and {@link MessageSourceAware} beans.
* 除了标准额org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory的声明周期功能之外,应用上下文的实现可以
* 探测和调用ApplicationContextAwarebean,ResourceLoaderAware,ApplicationEventPublisherAware,MessageSourceAware。
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader
*/
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,
MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
/**
* Return the unique id of this application context.
* 返回应用上下文的id,没有则为null
* @return the unique id of the context, or {@code null} if none
*/
String getId();
/**
* Return a name for the deployed application that this context belongs to.
* 返回应用上下文所属的部署应用名称,默认为空字符串
* @return a name for the deployed application, or the empty String by default
*/
String getApplicationName();
/**
* Return a friendly name for this context.
* 返回上下文友好的展示name
* @return a display name for this context (never {@code null})
*/
String getDisplayName();
/**
* Return the timestamp when this context was first loaded.
* 返回上下文第一次加载的时间戳
* @return the timestamp (ms) when this context was first loaded
*/
long getStartupDate();
/**
* Return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent
* and this is the root of the context hierarchy.
* 返回父上下文,如果没有父上下文,或这个是上下文的跟,则返回null。
* @return the parent context, or {@code null} if there is no parent
*/
ApplicationContext getParent();
/**
* Expose AutowireCapableBeanFactory functionality for this context.
* 暴露上下文的AutowireCapableBeanFactory功能性
* <p>This is not typically used by application code, except for the purpose of
* initializing bean instances that live outside of the application context,
* applying the Spring bean lifecycle (fully or partly) to them.
* 应用编码中不建议使用此AutowireCapableBeanFactory,自动装配bean工厂,用于初始化生存在应用上下文外部的实例,
* 并完全或部分控制Spring的bean的声明周期。
* <p>Alternatively, the internal BeanFactory exposed by the
* {@link ConfigurableApplicationContext} interface offers access to the
* {@link AutowireCapableBeanFactory} interface too. The present method mainly
* serves as a convenient, specific facility on the ApplicationContext interface.
* 另外,内部的bean工厂通过ConfigurableApplicationContext接口提供了访问AutowireCapableBeanFactory的操作。
* 此方法主要是为应用上下文提供方便。
* <p><b>NOTE: As of 4.2, this method will consistently throw IllegalStateException
* after the application context has been closed.</b> In current Spring Framework
* versions, only refreshable application contexts behave that way; as of 4.2,
* all application context implementations will be required to comply.
* 需要注意的是,在spring4.2版本中,当应用上下文关闭的时候,此方法将会抛出IllegalStateException。
* 在当前spring4.3.x框架的版本中,仅仅可刷新应用上下行为相同;在spring4.2中,所有的应用上下文的实现都行遵守
* 此规则。
* @return the AutowireCapableBeanFactory for this context
* 返回上下文的AutowireCapableBeanFactory
* @throws IllegalStateException if the context does not support the
* {@link AutowireCapableBeanFactory} interface, or does not hold an
* autowire-capable bean factory yet (e.g. if {@code refresh()} has
* never been called), or if the context has been closed already
* 如果上下文不支持AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口,或者没有持有一个可刷新的AutowireCapableBeanFactory实例,
* 即{@code refresh()还没有被调用的,或者上下文件已经关闭,则抛出IllegalStateException。
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()
* @see ConfigurableApplicationContext#getBeanFactory()
*/
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
从上,我们可以看出,ApplicationContext接口主要提供了获取父上下文,自动装配bean工厂 AutowireCapableBeanFactory,应用上下文name,展示name,启动时间戳及应用id的操作。应用上下文继承了 EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver ,具有了访问bean容器中组件, 配置环境,加载文件或类路径资源,发布应用事件到监听器,已经解决国际化消息的功能。另外需要注意的是,应用上下文具有,父上下文的继承性(HierarchicalBeanFactory)。定义在子孙上下文中的bean定义将会有限考虑。这意味着,一个单独的父上下文可以被整个web应用上下文所使用。这一点体现在,当我们使用spring的核心容器特性和spring mvc时,在web.xml中,我们有两个配置一个是上下文监听器(org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener),同时需要配置应用上下文bean的定义配置,一般是ApplicationContext.xml,另一个是Servlet分发器(org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet), 同时需要配置WebMVC相关配置,一般是springmvc.xml。应用一般运行的在Web容器中,Web容器可以访问应用上下文,同时Web容器的Servlet也可以访问应用上下文,然而每个servlet有自己的上下文,独立于其他servlet。
最后以应用上下文接口的类图来结束本篇文章:
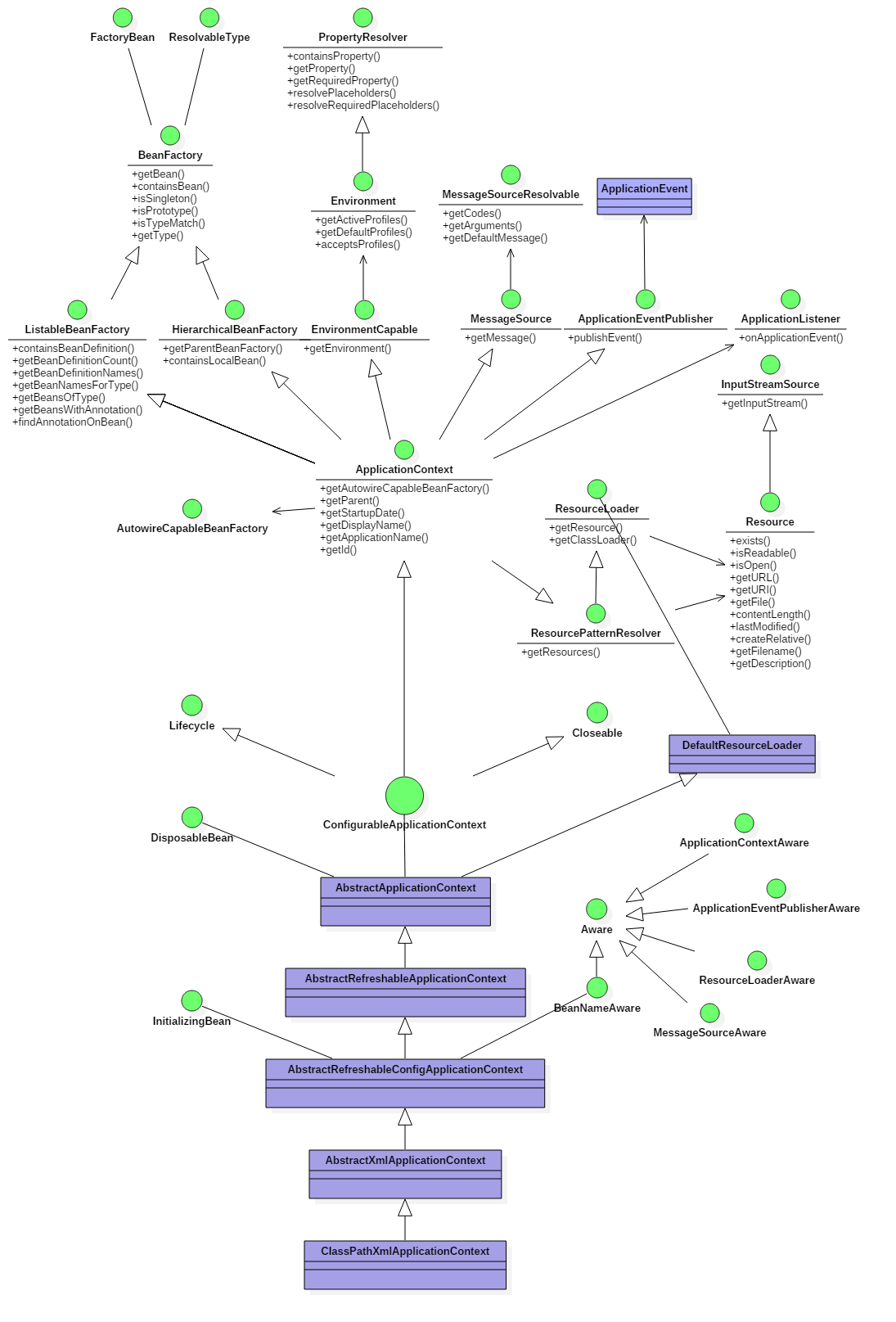
关于 AutowireCapableBeanFactory 我们将在下一篇文章中,再讲。
总结
BeanFactory接口主要是主要提供了根据名称或类型获取bean的相关方法,以及判断bean是否匹配指定类型或判断是否包含指定name的共享单实例或多实例bean。需要注意的是,如果bean工厂的实现是可继承工厂,那么调用这些方法,如果没有在当前bean工厂实例中找到,将会从父工厂中查到。另外还需要注意一点,判断一个bean是否为共享单例模式,可以使用isSingleton方法,返回true,即是,返回false,并不能表示bean是多实例bean,具体要用isPrototype方法判断,同理isPrototype方法也是如此。
ListableBeanFactory接口主要提供了判断是否存在给定name的bean定义,获取bean定义数量,获取指定类型的bean定义的name集或name与bean实例的映射集,获取待指定注解的bean定义的name或name与bean实例的映射集,以及获取给定name对应的bean的注定注解实例。需要注意的是,提供的操作不会到可继承bean工厂中去搜索,但包括BeanFactoryUtils工具类获取bean工厂的祖先bean工厂。另外getBeanNamesForType和getBeanNamesForAnnotation方法可以通过includeNonSingletons和allowEagerInit, 控制搜索bean的作用域范围和是否初始化懒加载单例模式bean与工厂bean。
HierarchicalBeanFactory接口标志一个以可继承bean工厂,我们可以通过 ConfigurableBeanFactory 接口的 setParentBeanFactory 方法配置bean工厂的父类工厂,主要提供获取父工厂操作,以及判断在本地bean工厂中是否存在指定name对应的bean的操作,但忽略祖先上下文中的bean定义。
事件发布接口ApplicationEventPublisher,主要作为ApplicationContext的父接口,封装了事件发布功能,提供了事件发布功能。当事件发布时,通知所有注册到当前应用关注ApplicationEvent事件event的监听器,如果发布的事件不是 ApplicationEvent, 则将会包装成 PayloadApplicationEvent。
ApplicationEvent用于表示应用发生的事件,事件包括事件发生的时间和事件发生源。
监听器接口ApplicationListener,是基于标准JDK的观察者模式的接口java.util.EventListener, 从spring3.0以后,应用监听器需要声明关注的应用事件类型。当监听器注册到spring的应用上下文ApplicationContext时, 将会根据事件类型过滤监听器,匹配事件类型的监听器才会被通知。接口主要提供了处理事件操作。
EnvironmentCapable接口,表示包括或暴露一个Environment环境引用的组件。Spring的所有应用上下文都是EnvironmentCapable接口实现,用于应用上下文与环境交互。需要注意的是,ApplicationContext扩展了EnvironmentCapable接口,通过getEnvironment方法暴露环境配置;然而 ConfigurableApplicationContext 将会重定义getEnvironment方法,返回一个ConfigurableEnvironment。 两种方法带来的效果是,在环境配置Environment对象在 ConfigurableApplicationContext 可访问以前,都是自读的,可以理解为 ConfigurableApplicationContext 的getEnvironment方法返回的环境象时可修改的。接口提供了获取环境配置操作。
Environment接口同时是一个 PropertyResolver 接口,提供了获取激活配置 Profiles 和默认配置的操作,同时提供了判断配置是否激活操作。应用环境Environment有一个或多个配置 Profiles,配置可以理解为配置集或类型,比如开发,测试,体验,生产等环境。当应用存在需要引用属性的情况,我们可以从环境中获取,应为环境是一个 PropertyResolver。环境配置对象必须通过ConfigurableEnvironment接口进行配置,所有AbstractApplicationContext的子类,都可通过getEnvironment方法返回一个可配置环境接口ConfigurableEnvironment。
PropertyResolver才出现,PropertyResolver注意根据属性源,是否包含给定属性,获取相关属性的值及获取给定类型属性的值操作,同时提供了替换给定上文本中的引用属性“${…}”操作。
ResourcePatternResolver拓展了 ResourceLoader 接口,主要用于解决或加载给定路径下的资源文件,ResourcePatternResolver建议使用以 “classpath*:”为前缀,创建一个匹配class路径的所有资源。
ResourceLoader接口用于加载资源class路径或文件系统等类型资源,提供获取给定位置的资源操作和获取系统ClassLoader。ResourceLoader获取类加载器,首先获取当前线程类加载器,如果没有当前线程上下文,则使用当前类的类加载器,如果当前类没有类加载器,则获取系统的类加载器。
Resource实际为一个输入流资源 InputStreamSource 接口,主要提供了获取资源URL,URI,对应的文件,文件名,上次修改时间戳,文件描述符操作,以及判断资源是否存在,是否可读,是否打开等操作。需要注意的是在读取资源后,要关闭资源,以防内存泄漏。
InputStreamSource主要提供了获取底层物理资源对应的输入流操作。
MessageSource接口提供了获取指定 Locale 的消息操作,消息支持占位符和国际化。同时提供了解决 MessageSourceResolvable 中的消息。
MessageSourceResolvable主要用于MessageSource接口的消息解决,提供了获取消息code,参数及默认消息操作。
ApplicationContext接口主要提供了获取父上下文,自动装配bean工厂 AutowireCapableBeanFactory,应用上下文name,展示name,启动时间戳及应用id的操作。应用上下文继承了 EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory,MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver ,具有了访问bean容器中组件, 配置环境,加载文件或类路径资源,发布应用事件到监听器,已经解决国际化消息的功能。另外需要注意的是,应用上下文具有,父上下文的继承性(HierarchicalBeanFactory)。定义在子孙上下文中的bean定义将会有限考虑。这意味着,一个单独的父上下文可以被整个web应用上下文所使用。这一点体现在,当我们使用spring的核心容器特性和spring mvc时,在web.xml中,我们有两个配置一个是上下文监听器(org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener),同时需要配置应用上下文bean的定义配置,一般是ApplicationContext.xml,另一个是Servlet分发器(org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet), 同时需要配置WebMVC相关配置,一般是springmvc.xml。应用一般运行的在Web容器中,Web容器可以访问应用上下文,同时Web容器的Servlet也可以访问应用上下文,然而每个servlet有自己的上下文,独立于其他servlet。
附
ResourceUtils
public abstract class ResourceUtils {
/** Pseudo URL prefix for loading from the class path: "classpath:" */
public static final String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = "classpath:";
/** URL prefix for loading from the file system: "file:" */
public static final String FILE_URL_PREFIX = "file:";
/** URL prefix for loading from a jar file: "jar:" */
public static final String JAR_URL_PREFIX = "jar:";
/** URL prefix for loading from a war file on Tomcat: "war:" */
public static final String WAR_URL_PREFIX = "war:";
/** URL protocol for a file in the file system: "file" */
public static final String URL_PROTOCOL_FILE = "file";
/** URL protocol for an entry from a jar file: "jar" */
public static final String URL_PROTOCOL_JAR = "jar";
/** URL protocol for an entry from a war file: "war" */
public static final String URL_PROTOCOL_WAR = "war";
/** URL protocol for an entry from a zip file: "zip" */
public static final String URL_PROTOCOL_ZIP = "zip";
/** URL protocol for an entry from a WebSphere jar file: "wsjar" */
public static final String URL_PROTOCOL_WSJAR = "wsjar";
/** URL protocol for an entry from a JBoss jar file: "vfszip" */
public static final String URL_PROTOCOL_VFSZIP = "vfszip";
/** URL protocol for a JBoss file system resource: "vfsfile" */
public static final String URL_PROTOCOL_VFSFILE = "vfsfile";
/** URL protocol for a general JBoss VFS resource: "vfs" */
public static final String URL_PROTOCOL_VFS = "vfs";
/** File extension for a regular jar file: ".jar" */
public static final String JAR_FILE_EXTENSION = ".jar";
/** Separator between JAR URL and file path within the JAR: "!/" */
public static final String JAR_URL_SEPARATOR = "!/";
/** Special separator between WAR URL and jar part on Tomcat */
public static final String WAR_URL_SEPARATOR = "*/";
}